Adding Intelligence to Your Blazor Apps Using Telerik Smart Components

Summarize with AI:
Learn about the Telerik Smart Components and how to use them in a Blazor app to leverage AI for better user experiences.
In a previous post, I told you about what Smart Components are and how you can integrate them into an existing Blazor application. In this post, you will see how companies like Progress have taken the concept to a new level by creating smart components that allow users to have more powerful experiences when using AI models. Let’s get started!
What Are Telerik Smart (AI) Components?
The Progress Telerik Smart (AI) Components are a set of experimental components that allow you to add AI features to your .NET applications. Telerik has created a series of intelligent components targeting different platforms such as Blazor, ASP.NET Core, WPF, WinForms and .NET MAUI.
It is very important that if you have any feedback on the components, you help the team shape their future through the Telerik Smart Components repository on GitHub.
Creating and Configuring a Project to Use Telerik Smart (AI) Components
The first step to turning Telerik components into intelligent ones is to properly configure the project to utilize the capabilities of embeddings and AI models within the project. To do this, we will install the following set of NuGet packages in the project:
Azure.AI.OpenAIMicrosoft.Extensions.AIMicrosoft.Extensions.AI.OpenAISmartComponents.LocalEmbeddings
The first package will help us connect to the Azure OpenAI service (you can use another one if you prefer). The second and third are wrappers that make it easier to create chat clients and inject them throughout the application pages. The last package contains classes that allow you to create embeddings and perform semantic comparisons locally (although it’s perfectly valid to use a vector database for this purpose).
The next step is to follow the Telerik Blazor Components installation guide in the project to easily copy and paste the code shown in the following sections. Let’s take a look at the first Telerik Smart Component that will help you implement AI in Data Grid-like components next.
The Grid Smart (AI) Search Component
This Smart Component is based on the Telerik Blazor Data Grid component, which allows you to visualize data with useful features such as filtering, sorting, pagination, etc. Let’s see how to turn a Data Grid into a Grid Smart (AI) Search.
Creating a Page with Text Search
Let’s assume that in the project we need to display products from an online store, retrieving the products from a REST API. Below, I will show you the files you should create to follow this demo:
ProductSearch.razor (Page Component)
@page "/product-search"
<PageTitle>Product Catalog</PageTitle>
@inject ProductCatalogService productService
<div class="demo-alert demo-alert-info">
<p>Browse our complete product catalog with <strong>@TotalProducts products</strong> across different categories!</p>
</div>
<TelerikGrid @ref="@GridRef"
Data=@GridData
Height="700px"
Pageable=true
PageSize="12"
Sortable="true">
<GridToolBarTemplate>
<div class="search-container">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Search" Class="search-icon"></TelerikSvgIcon>
Product Search
<TelerikTextBox @bind-Value="@FilterValue" Placeholder="Search by name, description, category, price..." Class="search-input">
</TelerikTextBox>
<TelerikButton OnClick="@Search" Icon="@SvgIcon.Search" ThemeColor="@ThemeConstants.Button.ThemeColor.Primary">Search</TelerikButton>
<TelerikButton OnClick="@ClearSearch" Icon="@SvgIcon.X" ThemeColor="@ThemeConstants.Button.ThemeColor.Secondary">Clear</TelerikButton>
</div>
</GridToolBarTemplate>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.ImageUrl) Title="Image" Width="100px" Sortable="false">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-image-container">
<img src="@product.ImageUrl" alt="@product.Title" class="product-image" />
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.Title) Title="Product" Width="250px">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-info">
<strong class="product-title">@product.Title</strong>
<div class="product-category">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.InfoCircle"></TelerikSvgIcon>
@product.CategoryFormatted
</div>
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.ShortDescription) Title="Description" Width="300px">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-description">
@product.ShortDescription
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.Price) Title="Price" Width="120px">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-price">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Dollar"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="price-value">@product.DisplayPrice</span>
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.Rating.Rate) Title="Rating" Width="140px">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-rating">
<div class="stars">@product.StarRating</div>
<div class="rating-details">
<span class="rating-value">@product.Rating.Rate.ToString("F1")</span>
<span class="rating-count">(@product.Rating.Count)</span>
</div>
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(ProductCatalogDto.Id) Title="Actions" Width="120px" Sortable="false">
<Template>
@{
var product = context as ProductCatalogDto;
}
<div class="product-actions">
<TelerikButton Icon="@SvgIcon.Cart"
Size="@ThemeConstants.Button.Size.Small"
ThemeColor="@ThemeConstants.Button.ThemeColor.Success"
OnClick="@(() => AddToCart(product))"
Title="Add to Cart">
</TelerikButton>
</div>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</TelerikGrid>
@if (IsLoading)
{
<div class="loading-overlay">
<div class="loading-content">
<TelerikLoader Visible="true"
Size="@ThemeConstants.Loader.Size.Large"
ThemeColor="@ThemeConstants.Loader.ThemeColor.Primary"></TelerikLoader>
<p class="loading-text">Loading product catalog...</p>
</div>
</div>
}
@code {
private string FilterValue { get; set; } = "";
private bool IsLoading { get; set; } = true;
private int TotalProducts { get; set; } = 0;
public TelerikGrid<ProductCatalogDto>? GridRef { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ProductCatalogDto> GridData { get; set; } = new List<ProductCatalogDto>();
public IEnumerable<ProductCatalogDto> AllProducts { get; set; } = new List<ProductCatalogDto>();
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
IsLoading = true;
StateHasChanged();
try
{
AllProducts = await productService.GetAllProductsAsync();
var allProductsJson = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(AllProducts, new System.Text.Json.JsonSerializerOptions { WriteIndented = true });
GridData = AllProducts;
TotalProducts = AllProducts.Count();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error loading products: {ex.Message}");
}
finally
{
IsLoading = false;
StateHasChanged();
}
}
private async Task Search()
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(FilterValue))
{
await ClearSearch();
return;
}
IsLoading = true;
StateHasChanged();
try
{
var searchResults = PerformTextSearch(FilterValue);
GridData = searchResults;
}
finally
{
IsLoading = false;
StateHasChanged();
}
}
private async Task ClearSearch()
{
FilterValue = "";
GridData = AllProducts;
StateHasChanged();
await Task.CompletedTask;
}
private List<ProductCatalogDto> PerformTextSearch(string query)
{
var searchTerm = query.ToLowerInvariant();
return AllProducts.Where(p =>
p.Title.ToLowerInvariant().Contains(searchTerm) ||
p.Description.ToLowerInvariant().Contains(searchTerm) ||
p.CategoryFormatted.ToLowerInvariant().Contains(searchTerm) ||
p.Price.ToString().Contains(searchTerm) ||
p.DisplayPrice.ToLowerInvariant().Contains(searchTerm)
).ToList();
}
private void AddToCart(ProductCatalogDto product)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Added {product.Title} to cart - ${product.Price}");
}
}
<style>
.demo-alert.demo-alert-info {
margin: 5px auto 15px;
padding: 15px 20px;
background-color: #e3f2fd;
border: 1px solid #2196f3;
border-radius: 4px;
color: #1565c0;
}
.toolbar-container {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10px;
padding: 10px 0;
font-size: 1.1em;
color: #333;
}
.toolbar-icon {
color: #666;
font-size: 1.2em;
}
.search-container {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
padding: 10px 0;
}
.search-icon {
color: #666;
}
.search-input {
min-width: 400px;
flex: 1;
}
.product-image-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
padding: 5px;
}
.product-image {
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
object-fit: cover;
border-radius: 4px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
.product-info {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 5px;
}
.product-title {
font-size: 1em;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.3;
}
.product-category {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 5px;
font-size: 0.85em;
color: #666;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
padding: 2px 6px;
border-radius: 12px;
width: fit-content;
}
.product-description {
color: #555;
font-size: 0.9em;
line-height: 1.4;
}
.product-price {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 5px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #1976d2;
font-size: 1.1em;
}
.price-value {
font-family: monospace;
}
.product-rating {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 3px;
}
.stars {
color: #ffc107;
font-size: 1.1em;
letter-spacing: 1px;
}
.rating-details {
font-size: 0.85em;
color: #666;
}
.rating-value {
font-weight: bold;
color: #333;
}
.rating-count {
color: #888;
}
.product-actions {
display: flex;
gap: 5px;
justify-content: center;
}
.loading-overlay {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.8);
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
z-index: 1000;
backdrop-filter: blur(2px);
}
.loading-content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
gap: 15px;
}
.loading-text {
margin: 0;
font-size: 1.1rem;
color: #666;
font-weight: 500;
}
</style>
ProductCatalogDto.cs - Product model
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
namespace TelerikSmartComponentsDemo.Models;
public class ProductCatalogDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("id")]
public int Id { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("title")]
public string Title { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("price")]
public decimal Price { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("description")]
public string Description { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("category")]
public string Category { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("image")]
public string ImageUrl { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("rating")]
public ProductRatingDto Rating { get; set; } = new();
public string DisplayPrice => $"${Price:F2}";
public string ShortDescription => Description.Length > 100 ? Description.Substring(0, 100) + "..." : Description;
public string CategoryFormatted => Category.Replace("'", "").Replace(" ", " ").ToTitleCase();
public string SearchText => $"{Title} {Description} {Category} ${Price} {Rating.Rate} stars";
public string StarRating => new string('★', (int)Math.Round(Rating.Rate)) + new string('☆', 5 - (int)Math.Round(Rating.Rate));
}
public class ProductRatingDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("rate")]
public double Rate { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("count")]
public int Count { get; set; }
}
public static class StringExtensions
{
public static string ToTitleCase(this string input)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(input))
return input;
var words = input.Split(' ');
for (int i = 0; i < words.Length; i++)
{
if (words[i].Length > 0)
{
words[i] = char.ToUpper(words[i][0]) + (words[i].Length > 1 ? words[i].Substring(1).ToLower() : "");
}
}
return string.Join(" ", words);
}
}
ProductCatalogService.cs - Product retrieval service
public class ProductCatalogService
{
private readonly HttpClient _httpClient;
private readonly ILogger<ProductCatalogService> _logger;
private List<ProductCatalogDto>? _cachedProducts;
public ProductCatalogService(HttpClient httpClient, ILogger<ProductCatalogService> logger)
{
_httpClient = httpClient;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<ProductCatalogDto>> GetAllProductsAsync()
{
if (_cachedProducts != null)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Returning cached product data");
return _cachedProducts;
}
try
{
_logger.LogInformation("Fetching products from Fake Store API...");
var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync("https://fakestoreapi.com/products");
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var jsonContent = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var products = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<ProductCatalogDto>>(jsonContent, new JsonSerializerOptions
{
PropertyNameCaseInsensitive = true
});
if (products != null && products.Any())
{
_cachedProducts = products;
_logger.LogInformation($"Successfully loaded {products.Count} products from API");
return products;
}
}
else
{
_logger.LogWarning($"API request failed with status: {response.StatusCode}");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching products from Fake Store API");
}
_logger.LogInformation("Using mock product data as fallback");
return GetMockProducts();
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<ProductCatalogDto>> GetProductsByCategoryAsync(string category)
{
try
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Fetching products for category: {category}");
var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync($"https://fakestoreapi.com/products/category/{category}");
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var jsonContent = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var products = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<ProductCatalogDto>>(jsonContent, new JsonSerializerOptions
{
PropertyNameCaseInsensitive = true
});
if (products != null && products.Any())
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Successfully loaded {products.Count} products for category {category}");
return products;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, $"Error fetching products for category {category}");
}
var allMockProducts = GetMockProducts();
return allMockProducts.Where(p => p.Category.Equals(category, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<string>> GetCategoriesAsync()
{
try
{
var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync("https://fakestoreapi.com/products/categories");
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var jsonContent = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var categories = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<string>>(jsonContent);
if (categories != null && categories.Any())
{
return categories.Select(c => c.ToTitleCase());
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching categories");
}
return new[] { "Electronics", "Jewelery", "Men's Clothing", "Women's Clothing" };
}
private List<ProductCatalogDto> GetMockProducts()
{
return new List<ProductCatalogDto>
{
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 1,
Title = "iPhone 15 Pro Max",
Price = 1199.99m,
Description = "The latest iPhone with advanced camera system, A17 Pro chip, and titanium design. Features 6.7-inch Super Retina XDR display.",
Category = "electronics",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=iPhone+15",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.8, Count = 1250 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 2,
Title = "Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra",
Price = 1299.99m,
Description = "Premium Android smartphone with S Pen, 200MP camera, and AI-powered features. 6.8-inch Dynamic AMOLED display.",
Category = "electronics",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Galaxy+S24",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.7, Count = 980 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 3,
Title = "MacBook Pro 16-inch M3",
Price = 2499.99m,
Description = "Professional laptop with M3 chip, 16-inch Liquid Retina XDR display, and up to 22 hours of battery life.",
Category = "electronics",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=MacBook+Pro",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.9, Count = 750 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 4,
Title = "Sony WH-1000XM5 Headphones",
Price = 399.99m,
Description = "Industry-leading noise canceling wireless headphones with 30-hour battery life and crystal clear hands-free calling.",
Category = "electronics",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Sony+Headphones",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.6, Count = 2100 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 5,
Title = "Gold Diamond Ring",
Price = 899.99m,
Description = "Elegant 14k gold ring with natural diamonds. Perfect for engagements or special occasions. Comes with certificate of authenticity.",
Category = "jewelery",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Diamond+Ring",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.5, Count = 145 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 6,
Title = "Men's Casual Cotton T-Shirt",
Price = 29.99m,
Description = "Comfortable 100% cotton t-shirt in various colors. Perfect for everyday wear with a relaxed fit and soft fabric.",
Category = "men's clothing",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Cotton+Tshirt",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.2, Count = 890 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 7,
Title = "Women's Summer Dress",
Price = 79.99m,
Description = "Elegant floral summer dress made from breathable fabric. Features adjustable straps and a flattering A-line silhouette.",
Category = "women's clothing",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Summer+Dress",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.4, Count = 567 }
},
new ProductCatalogDto
{
Id = 8,
Title = "Wireless Gaming Mouse",
Price = 89.99m,
Description = "High-precision wireless gaming mouse with RGB lighting, programmable buttons, and 100-hour battery life.",
Category = "electronics",
ImageUrl = "https://via.placeholder.com/300x300?text=Gaming+Mouse",
Rating = new ProductRatingDto { Rate = 4.3, Count = 1200 }
}
};
}
}
Next, to avoid exceptions, we must register the product retrieval service in Program.cs, as well as HttpClient as follows:
...
builder.Services.AddScoped<ProductCatalogService>();
builder.Services.AddHttpClient();
var app = builder.Build();
...
Once the above is configured, we will be able to see the application in action. This application can perform textual searches but not semantic searches, as seen in the following image:
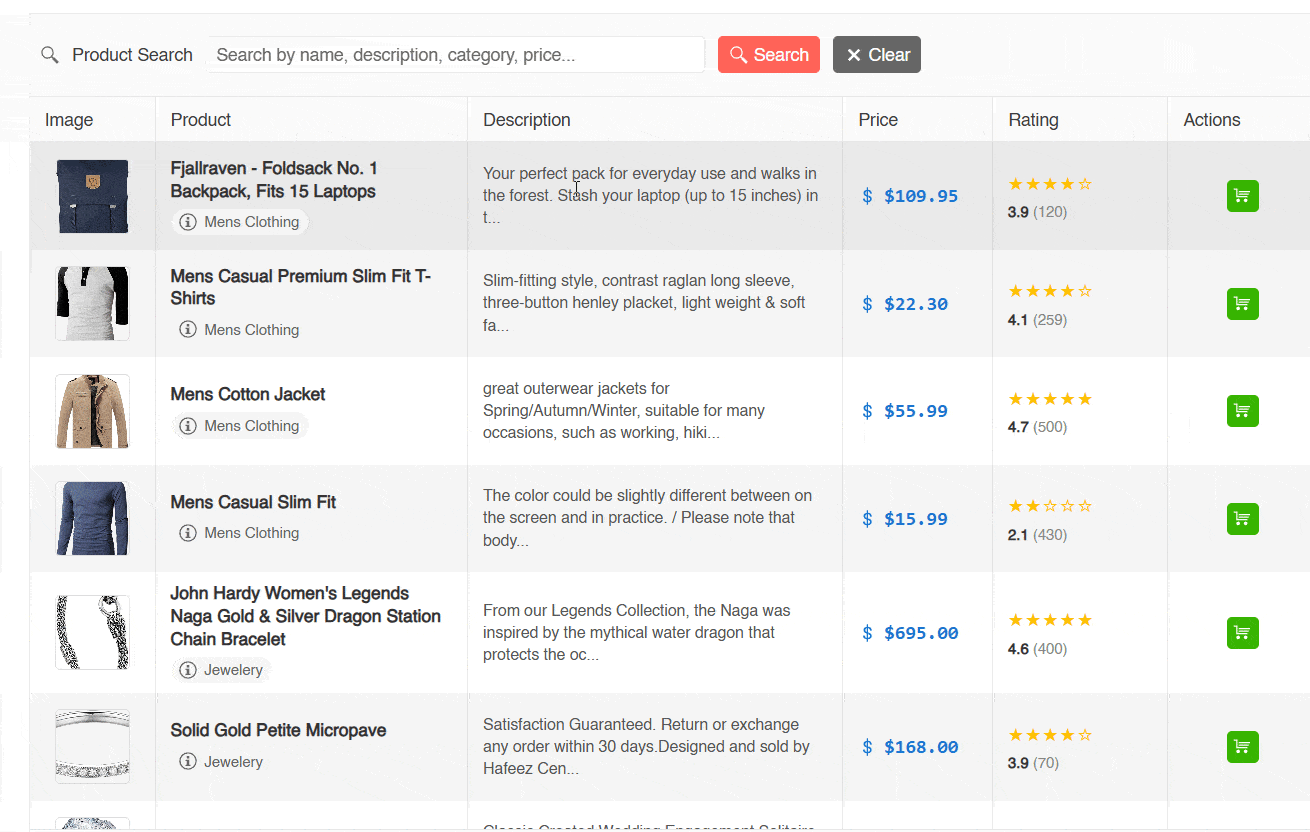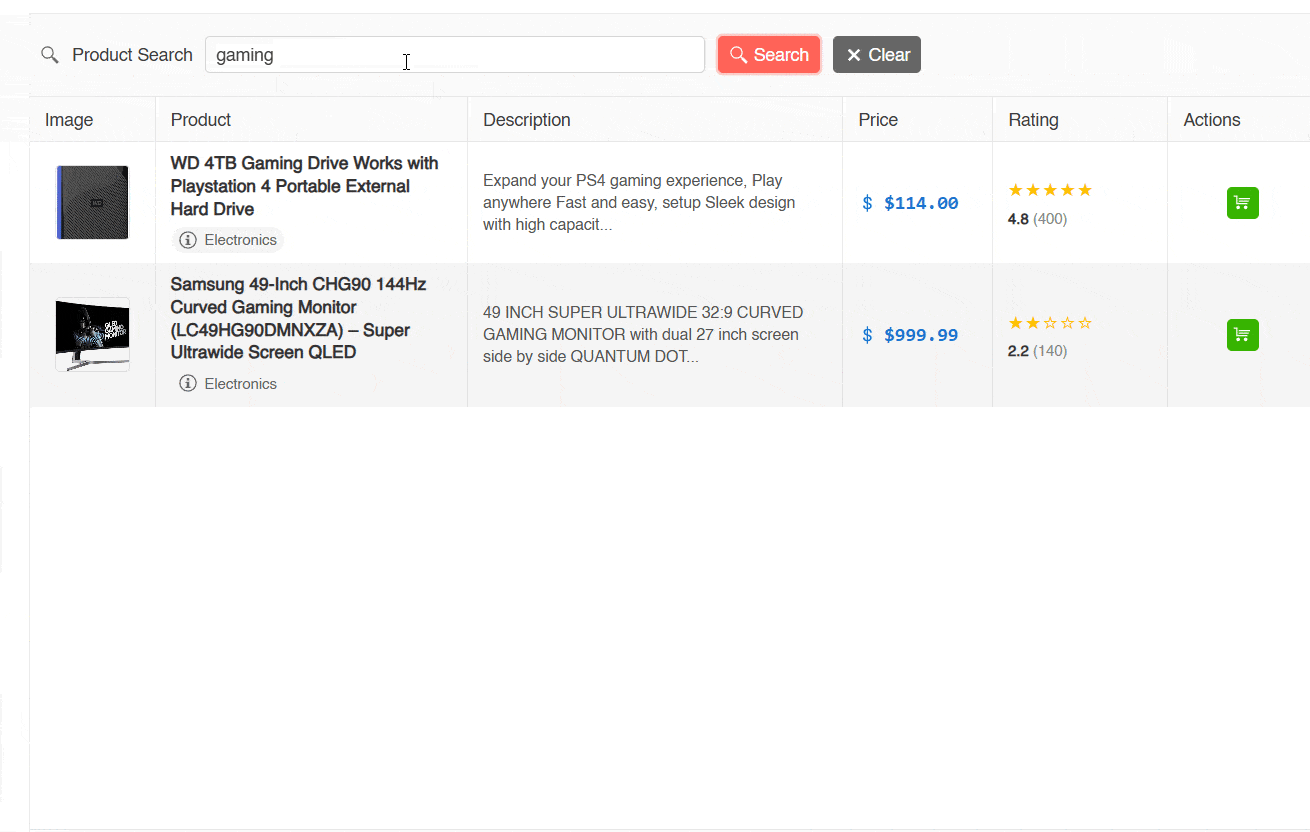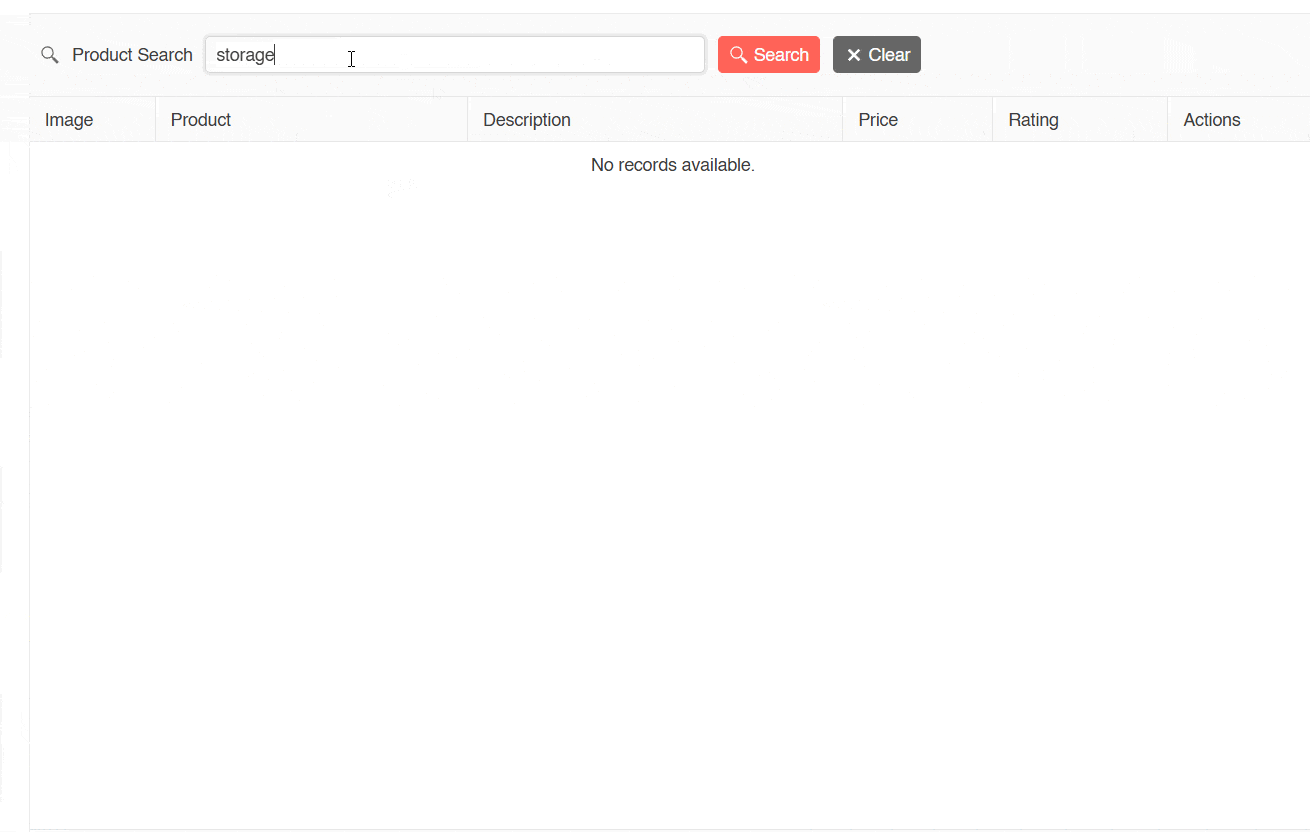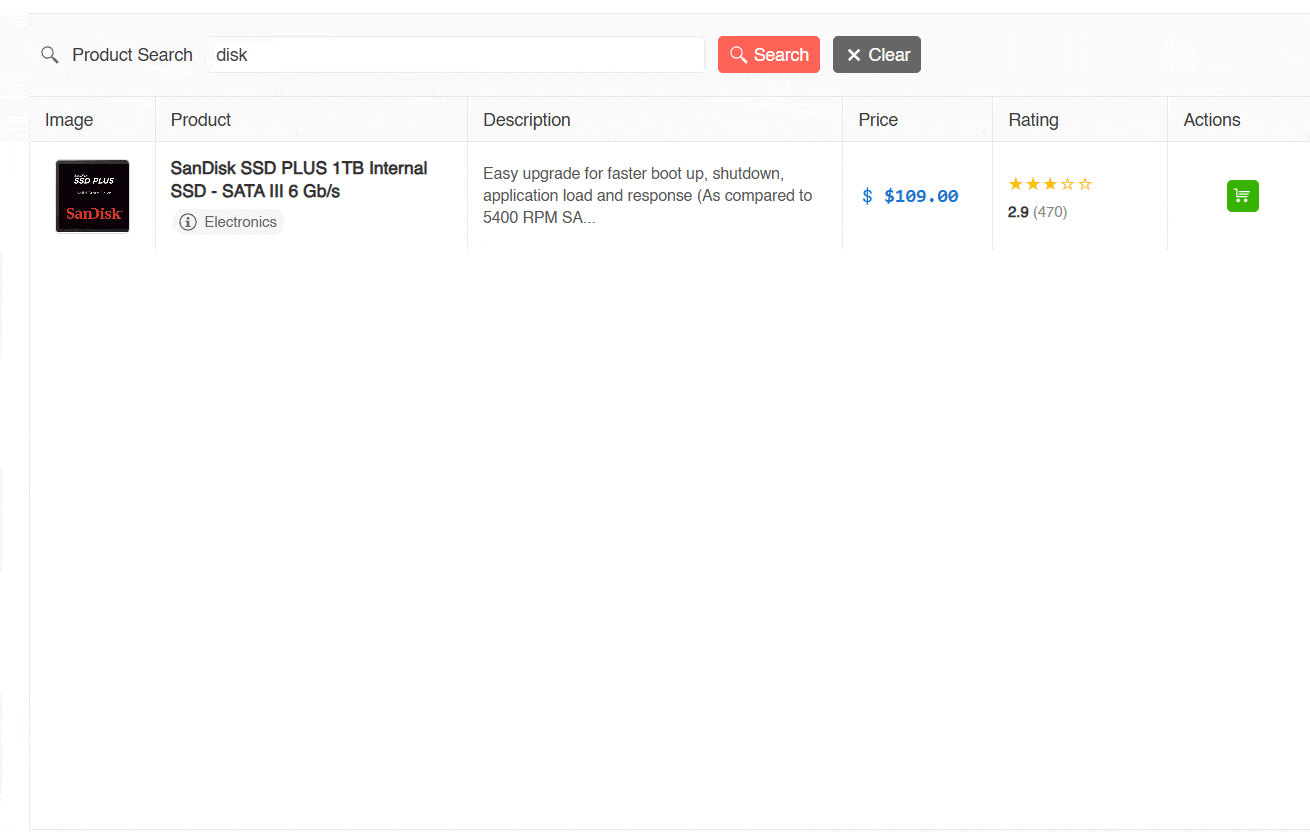
In the previous image, you can see how it is possible to perform a textual search for products with the terms gaming and disk, which returns results. However, when trying to perform a semantic search with the term storage (which is a semantic synonym of disk), no matches are shown. Let’s see how to improve this.
Creating Product Embeddings
To perform a semantic search on our page, it’s necessary to work with embeddings. Fortunately, the SmartComponents.LocalEmbeddings package contains everything needed to work with them. For this reason, in the code section of the project, we will add a new dictionary property that maps the Id of each product to its respective embedding, as follows:
@code {
..
Dictionary<int, EmbeddingF32>();
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
..
The EmbeddingF32 class allows storing embeddings in local memory, as well as performing similarity comparison operations that could be useful for grouping similar products, generating recommendations, or in our case, searching for items based on a search term.
Once we have the property that will allow us to store product embeddings, the next step is to extract the information from each product and convert it into an embedding. We will do this once the products have been retrieved from the REST service, as shown in the following example:
try
{
...
GridData = AllProducts;
using var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
foreach (var product in AllProducts)
{
ProductEmbeddings.Add(product.Id, embedder.Embed(product.SearchText));
}
...
}
In the previous code, a new element is added to the list of embeddings, with the product Id as the key. Next, the embedder’s Embed method is used to transform the product’s SearchText property into an embedding, which is stored as the value of the item in the dictionary. To convert all the product information such as Description, Category, Rating, etc. into an embedding, the SearchText property has been defined in the product model, which concatenates all the information as shown below:
public string SearchText => $"{Title} {Description} {Category} ${Price} {Rating.Rate} stars";
Now let’s see how to perform semantic searches.
Performing Semantic Searches in a Smart Grid (AI) Search
Once we have all the semantic information of the products in memory, it’s time to replace the content of the PerformTextSearch method, in order to eliminate the use of the Contains method that only performs textual searches.
The first thing we will do is create a new LocalEmbedder in order to reuse the Embed method, this time to obtain the embedding of the search term:
private List<ProductCatalogDto> PerformTextSearch(string query)
{
using var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
var queryVector = embedder.Embed(query);
}
Next, for demonstration purposes and to allow you to conduct tests, we will iterate through each product to see its similarity value against the search term in the Output window as follows:
...
foreach (var product in AllProducts)
{
var similarity = LocalEmbedder.Similarity(ProductEmbeddings[product.Id], queryVector);
Debug.WriteLine($"{product.Title} is {similarity:F3} similar to query: {query}");
}
...
Finally, we will perform filtering and sorting based on the similarity comparison, adding a threshold that indicates how much similarity we will apply. This result will be what we return in the method:
...
var threshold = 0.5;
return AllProducts
.Where(p => LocalEmbedder.Similarity(ProductEmbeddings[p.Id], queryVector) > threshold)
.OrderByDescending(p => LocalEmbedder.Similarity(ProductEmbeddings[p.Id], queryVector))
.ToList();
...
When running the page, we will have a result like the following:
-search-to-perform-semantic-searches.gif?sfvrsn=5e7073a8_2)
In the previous example, you can see that a semantic search is now being performed, as entering the term storage finds products that are related not only to hard drives but also to backpacks.
The Smart AI Search ComboBox Component
Another component that is also very useful and can become a smart component is the Telerik ComboBox for Blazor. To achieve this, we will follow a similar flow to what we saw with the Grid Smart (AI) Search component. Below, I will show you the classes to create a page where a user can get some cities with their weather, in order to later perform a semantic search:
WeatherDto.cs - Model of a city with its weather
public class WeatherDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("name")]
public string CityName { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("main")]
public WeatherMainDto Main { get; set; } = new();
[JsonPropertyName("weather")]
public List<WeatherDescriptionDto> Weather { get; set; } = new();
[JsonPropertyName("wind")]
public WeatherWindDto Wind { get; set; } = new();
[JsonPropertyName("sys")]
public WeatherSysDto Sys { get; set; } = new();
[JsonPropertyName("visibility")]
public int Visibility { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("dt")]
public long DateTime { get; set; }
public string DisplayName => $"{CityName}, {Sys.Country}";
public string Description => Weather.FirstOrDefault()?.Description ?? "No description";
public double Temperature => Main.Temp;
public string SearchText => $"{CityName} {Sys.Country} {Description} {Main.Temp}°C weather climate";
}
public class WeatherMainDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("temp")]
public double Temp { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("feels_like")]
public double FeelsLike { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("temp_min")]
public double TempMin { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("temp_max")]
public double TempMax { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("pressure")]
public int Pressure { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("humidity")]
public int Humidity { get; set; }
}
public class WeatherDescriptionDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("id")]
public int Id { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("main")]
public string Main { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("description")]
public string Description { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("icon")]
public string Icon { get; set; } = string.Empty;
}
public class WeatherWindDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("speed")]
public double Speed { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("deg")]
public int Deg { get; set; }
}
public class WeatherSysDto
{
[JsonPropertyName("country")]
public string Country { get; set; } = string.Empty;
[JsonPropertyName("sunrise")]
public long Sunrise { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("sunset")]
public long Sunset { get; set; }
}
WeatherService.cs - Weather Retrieval Service
In this file, you can add your own key if you want to get real data, or work with the fixed data:
public class WeatherService
{
private readonly HttpClient _http;
private readonly Dictionary<string, WeatherDto> _cachedWeather = new();
private readonly TimeSpan _cacheExpiry = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10);
// Get your free API key from: https://openweathermap.org/api
private const string API_KEY = "YOUR_OPENWEATHER_API_KEY_HERE"; // Replace with your actual API key
private const string BASE_URL = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5";
public WeatherService(HttpClient http)
{
_http = http;
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<WeatherDto>> GetWeatherForMultipleCitiesAsync()
{
var cities = new[] { "Reykjavik", "Singapore", "Seattle", "Cairo", "Bariloche", "Dubai", "Bali", "Tromsø", "Lima", "San Diego" };
var weatherData = new List<WeatherDto>();
foreach (var city in cities)
{
var weather = await GetWeatherByCityAsync(city);
if (weather != null)
{
weatherData.Add(weather);
}
}
return weatherData;
}
public async Task<WeatherDto?> GetWeatherByCityAsync(string city)
{
var cacheKey = $"{city}_{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd-HH}";
if (_cachedWeather.ContainsKey(cacheKey))
{
return _cachedWeather[cacheKey];
}
try
{
if (API_KEY == "YOUR_OPENWEATHER_API_KEY_HERE")
{
return GetMockWeatherForCity(city);
}
var url = $"{BASE_URL}/weather?q={Uri.EscapeDataString(city)}&appid={API_KEY}&units=metric";
var weather = await _http.GetFromJsonAsync<WeatherDto>(url);
if (weather != null)
{
_cachedWeather[cacheKey] = weather;
return weather;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error fetching weather for {city}: {ex.Message}");
return GetMockWeatherForCity(city);
}
return null;
}
private WeatherDto GetMockWeatherForCity(string city)
{
var random = new Random(city.GetHashCode()); // Consistent random data per city
var weatherTypes = new[]
{
("Clear", "clear sky"),
("Clouds", "few clouds"),
("Clouds", "scattered clouds"),
("Rain", "light rain"),
("Snow", "light snow")
};
var weatherType = weatherTypes[random.Next(weatherTypes.Length)];
var countries = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "New York", "US" }, { "London", "GB" }, { "Tokyo", "JP" },
{ "Paris", "FR" }, { "Sydney", "AU" }, { "Berlin", "DE" },
{ "Madrid", "ES" }, { "Rome", "IT" }, { "Amsterdam", "NL" }, { "Stockholm", "SE" }
};
return new WeatherDto
{
CityName = city,
Main = new WeatherMainDto
{
Temp = Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 35 - 5, 1), // -5 to 30°C
FeelsLike = Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 35 - 5, 1),
TempMin = Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 30 - 10, 1),
TempMax = Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 40 + 5, 1),
Humidity = random.Next(30, 90),
Pressure = random.Next(990, 1030)
},
Weather = new List<WeatherDescriptionDto>
{
new WeatherDescriptionDto
{
Main = weatherType.Item1,
Description = weatherType.Item2,
Icon = "01d"
}
},
Wind = new WeatherWindDto
{
Speed = Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 15, 1),
Deg = random.Next(0, 360)
},
Sys = new WeatherSysDto
{
Country = countries.GetValueOrDefault(city, "XX"),
Sunrise = DateTimeOffset.Now.ToUnixTimeSeconds() - 6 * 3600,
Sunset = DateTimeOffset.Now.ToUnixTimeSeconds() + 6 * 3600
},
Visibility = random.Next(5000, 10000),
DateTime = DateTimeOffset.Now.ToUnixTimeSeconds()
};
}
}
Additionally, remember to add the WeatherService dependency container in Program.cs:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
builder.Services.AddScoped<WeatherService>();
...
var app = builder.Build();
Finally, add a new page to your project. In my case, it is called WeatherSmartAISearch.razor, which looks as follows:
@page "/weather-smart-ai-search"
<PageTitle>Weather Smart AI Search Demo</PageTitle>
@inject WeatherService weatherService
<div class="demo-alert demo-alert-info">
<p>Try typing <strong>"sunny"</strong>, <strong>"cold"</strong>, <strong>"rain"</strong>, or <strong>"warm weather"</strong> in the combobox to see how our smart search works with weather data!</p>
</div>
<div class="weather-search-container">
<h4>Find Cities by Weather Conditions</h4>
<TelerikComboBox @bind-Value="@SelectedWeatherId"
TItem="@WeatherDto" TValue="@string"
OnRead="@ReadWeatherItems"
Placeholder="Search for weather conditions (e.g., sunny, rainy, cold)"
ValueField="@nameof(WeatherDto.CityName)"
TextField="@nameof(WeatherDto.DisplayName)"
Filterable="true"
ShowClearButton="true"
Width="400px">
<ItemTemplate>
@{
var weather = context as WeatherDto;
}
<div class="weather-item">
<div class="weather-city">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.MapMarker"></TelerikSvgIcon>
@weather.DisplayName
</div>
<div class="weather-details">
<span class="weather-temp">@weather.Temperature.ToString("F1")°C</span>
<span class="weather-desc">@weather.Description</span>
</div>
</div>
</ItemTemplate>
</TelerikComboBox>
@if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(SelectedWeatherId) && SelectedWeather != null)
{
<div class="weather-details-card">
<TelerikCard>
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Cloud"></TelerikSvgIcon>
Weather in @SelectedWeather.DisplayName
</CardTitle>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody>
<div class="weather-info-grid">
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.InfoCircle"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Temperature:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Temperature.ToString("F1")°C</span>
</div>
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Eye"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Feels like:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Main.FeelsLike.ToString("F1")°C</span>
</div>
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Droplet"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Humidity:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Main.Humidity%</span>
</div>
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.InfoCircle"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Pressure:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Main.Pressure hPa</span>
</div>
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.InfoCircle"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Wind:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Wind.Speed.ToString("F1") m/s</span>
</div>
<div class="weather-info-item">
<TelerikSvgIcon Icon="@SvgIcon.Cloud"></TelerikSvgIcon>
<span class="label">Condition:</span>
<span class="value">@SelectedWeather.Description</span>
</div>
</div>
</CardBody>
</TelerikCard>
</div>
}
</div>
@if (IsLoading)
{
<div class="loading-container">
<div class="loading-content">
<TelerikLoader Visible="true"
Size="@ThemeConstants.Loader.Size.Large"
ThemeColor="@ThemeConstants.Loader.ThemeColor.Primary"></TelerikLoader>
<p class="loading-text">Loading weather data...</p>
</div>
</div>
}
@code {
private string SelectedWeatherId { get; set; } = "";
private bool IsLoading { get; set; } = true;
public IEnumerable<WeatherDto> AllWeatherData { get; set; } = new List<WeatherDto>();
public Dictionary<string, EmbeddingF32> WeatherEmbeddings { get; set; } = new Dictionary<string, EmbeddingF32>();
public WeatherDto? SelectedWeather => AllWeatherData.FirstOrDefault(w => w.CityName == SelectedWeatherId);
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
IsLoading = true;
StateHasChanged();
try
{
AllWeatherData = await weatherService.GetWeatherForMultipleCitiesAsync();
using var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
foreach (var weather in AllWeatherData)
{
WeatherEmbeddings.Add(weather.CityName, embedder.Embed(weather.SearchText));
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error loading weather data: {ex.Message}");
}
finally
{
IsLoading = false;
StateHasChanged();
}
}
protected void ReadWeatherItems(ComboBoxReadEventArgs args)
{
if (args.Request.Filters.Count > 0)
{
var filter = args.Request.Filters[0] as Telerik.DataSource.FilterDescriptor;
string userInput = filter?.Value?.ToString() ?? "";
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(userInput))
{
var searchResults = PerformSmartWeatherSearch(userInput);
args.Data = searchResults;
}
else
{
args.Data = AllWeatherData;
}
}
else
{
args.Data = AllWeatherData;
}
}
public List<WeatherDto> PerformSmartWeatherSearch(string query)
{
using var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
var queryVector = embedder.Embed(query);
foreach (var weather in AllWeatherData)
{
var similarity = LocalEmbedder.Similarity(WeatherEmbeddings[weather.CityName], queryVector);
Console.WriteLine($"{weather.DisplayName} ({weather.Description}) is {similarity:F3} similar to query: {query}");
}
var threshold = 0.6;
return AllWeatherData
.Where(w => LocalEmbedder.Similarity(WeatherEmbeddings[w.CityName], queryVector) > threshold)
.OrderByDescending(w => LocalEmbedder.Similarity(WeatherEmbeddings[w.CityName], queryVector))
.ToList();
}
}
<style>
.demo-alert.demo-alert-info {
margin: 5px auto 15px;
padding: 15px 20px;
background-color: #e3f2fd;
border: 1px solid #2196f3;
border-radius: 4px;
color: #1565c0;
}
.weather-search-container {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
}
.weather-search-container h4 {
margin-bottom: 20px;
color: #333;
}
.weather-item {
padding: 8px 0;
}
.weather-city {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 8px;
font-weight: 500;
color: #333;
margin-bottom: 4px;
}
.weather-details {
display: flex;
gap: 15px;
font-size: 0.9em;
color: #666;
margin-left: 24px;
}
.weather-temp {
font-weight: 500;
color: #1976d2;
}
.weather-desc {
font-style: italic;
}
.weather-details-card {
margin-top: 30px;
}
.weather-info-grid {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(200px, 1fr));
gap: 15px;
}
.weather-info-item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 8px;
padding: 8px;
background-color: #f8f9fa;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.weather-info-item .label {
font-weight: 500;
color: #555;
}
.weather-info-item .value {
color: #1976d2;
font-weight: 500;
}
.loading-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 200px;
}
.loading-content {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
gap: 15px;
}
.loading-text {
margin: 0;
font-size: 1.1rem;
color: #666;
font-weight: 500;
}
</style>
With the modified code, the result is as follows:
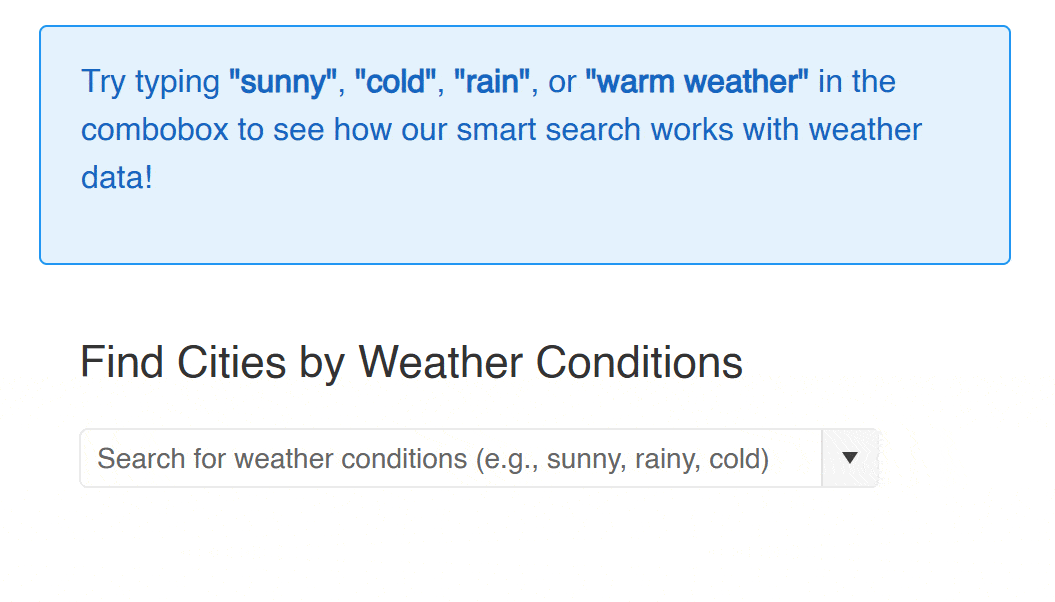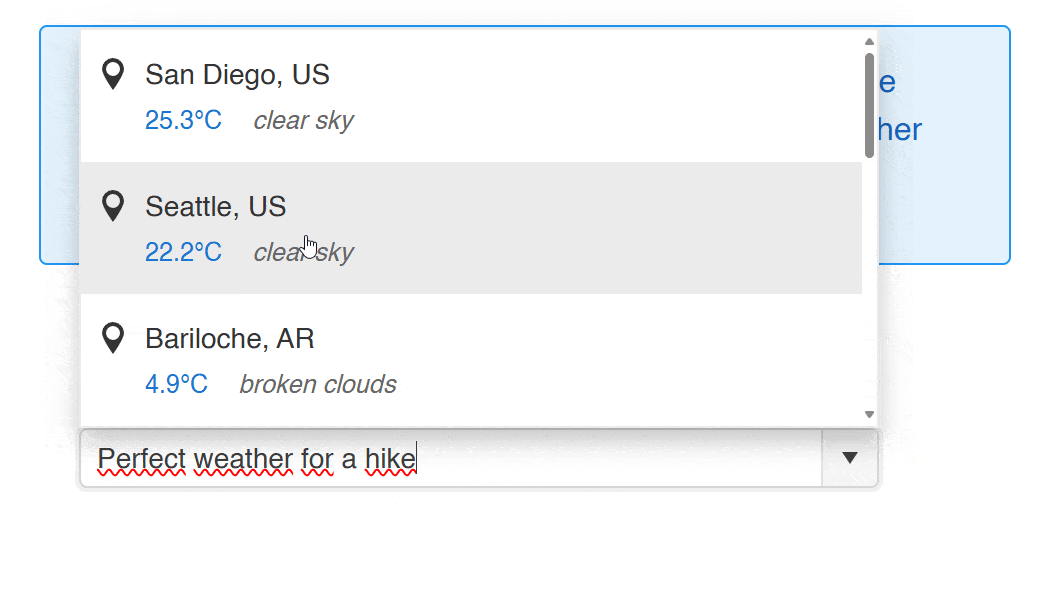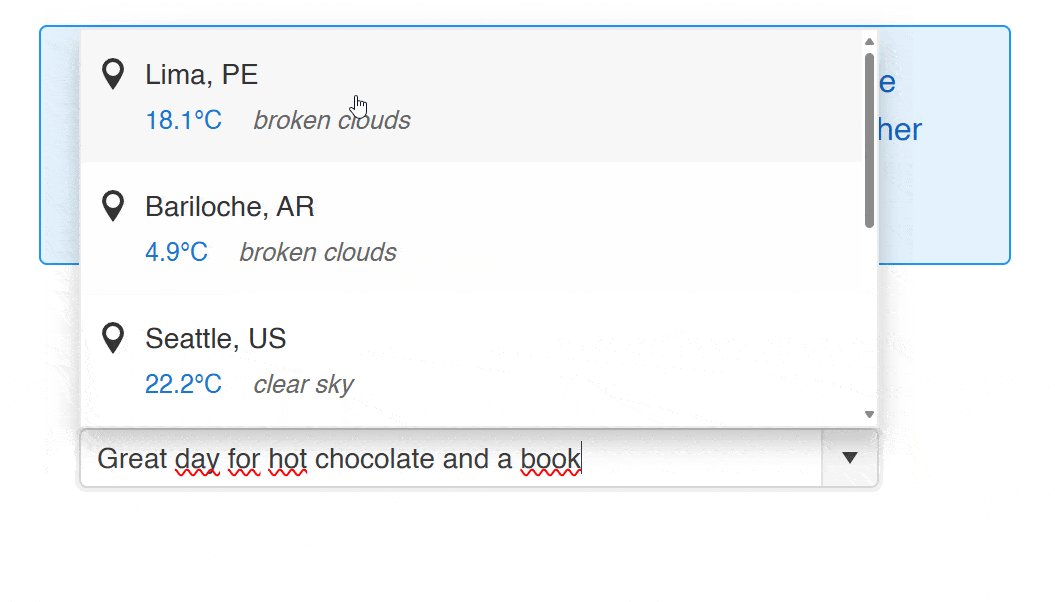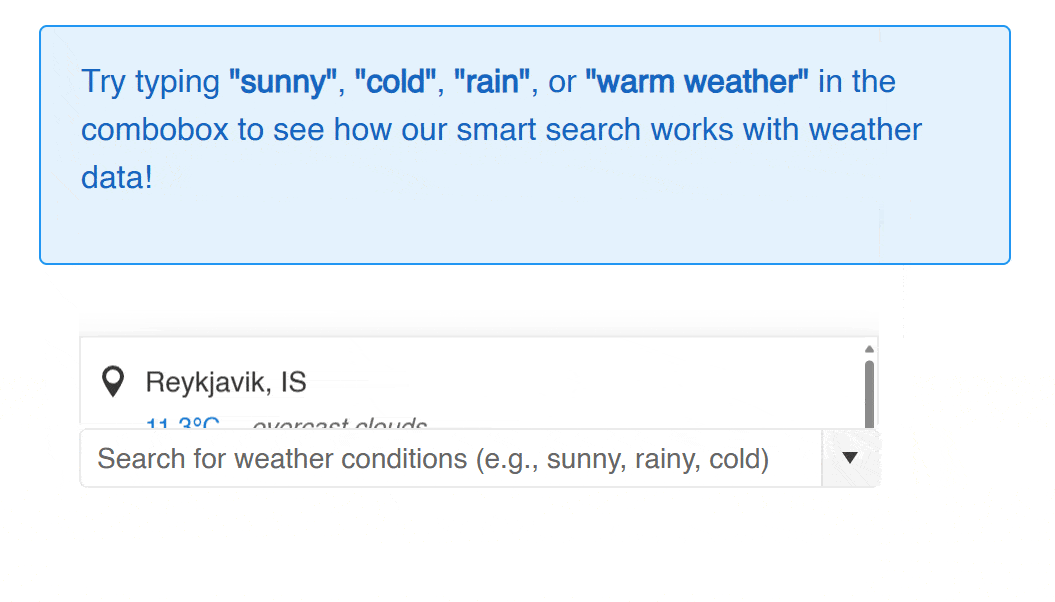
Within the component, you can notice that the following flow is followed:
- A dictionary property of type
Dictionary<string, EmbeddingF32>is created. - For each weather result, a local embedding is created and added to the embeddings dictionary.
- When performing a search, the embedding of the text to search is created and a similarity query is executed to return similar results.
Now, let’s work with PDFViewer Smart AI Assistant.
The PDFViewer Smart AI Assistant Component
The last component we will examine is the PDFViewer Smart AI Assistant, which is useful for helping users answer questions they may have about a PDF document. For this control to work correctly, you need to add an AI model of your choice to work alongside the context found according to any questions users may have.
Let’s start by configuring Program.cs, registering and configuring ChatClient to work with a deployment in Azure OpenAI:
var key = builder.Configuration["AzureOPENAI:Key"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
{
builder.Services
.AddChatClient(new AzureOpenAIClient(
new Uri("your-deployment-endpoint"),
new ApiKeyCredential(key))
.GetChatClient("your-deployment-name").AsIChatClient());
}
else
{
Debug.WriteLine("Warning: AzureOPENAI:Key not configured. AI features will not be available.");
}
var app = builder.Build();
In the above code, the service key is obtained from the environment variables, while the deployment endpoint and its name are specified manually, although you can configure this to get the information from wherever you prefer.
The next step is to add a PDF document containing text to your project. In my example, I added it to the wwwroot folder for local loading purposes. Although I am doing it this way, you can load it from an external URL, read some dynamically generated document, etc.
Next, create a new page-type component, in my case, I’ve called it PdfViewerSmart.razor with the following code:
@page "/pdfviewer"
@inject IChatClient ChatClient
@inject NavigationManager NavigationManager
@inject HttpClient Http
<PageTitle>PdfViewer Smart AI Assistant Demo</PageTitle>
@inject IJSRuntime jsRuntime
<div class="demo-alert demo-alert-info">
<p>To run the demo configure your AI API credentials inside <code>CallOpenAIApi()</code> method.</p>
</div>
<TelerikPdfViewer @ref="@PdfViewerRef"
Width="100%"
Height="800px"
Data="@FileData">
<PdfViewerToolBar>
<PdfViewerToolBarCustomTool>
<TelerikButton Id="ai-button" OnClick="@ToggleAIPrompt" Icon="SvgIcon.Sparkles">AI Assistant</TelerikButton>
<TelerikPopup @ref="@PopupRef"
AnimationDuration="300"
AnimationType="@AnimationType.SlideUp"
AnchorHorizontalAlign="@PopupAnchorHorizontalAlign.Left"
AnchorVerticalAlign="@PopupAnchorVerticalAlign.Bottom"
AnchorSelector="#ai-button"
HorizontalAlign="@PopupHorizontalAlign.Left"
VerticalAlign="@PopupVerticalAlign.Top"
Class="ai-prompt-popup"
Width="420px"
Height="400px">
<TelerikAIPrompt OnPromptRequest="@HandlePromptRequest"
PromptSuggestions="@PromptSuggestions">
</TelerikAIPrompt>
</TelerikPopup>
</PdfViewerToolBarCustomTool>
</PdfViewerToolBar>
</TelerikPdfViewer>
@code {
public TelerikPdfViewer PdfViewerRef { get; set; }
public byte[] FileData { get; set; }
public List<string> PromptSuggestions { get; set; }
public bool IsAIPromptPopupVisible { get; set; }
public TelerikPopup PopupRef { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, EmbeddingF32> PageEmbeddings { get; set; }
public string[] TextInChunks { get; set; }
bool firstRender = true;
private void ToggleAIPrompt()
{
if (IsAIPromptPopupVisible)
{
PopupRef.Hide();
}
else
{
PopupRef.Show();
}
IsAIPromptPopupVisible = !IsAIPromptPopupVisible;
}
private async Task HandlePromptRequest(AIPromptPromptRequestEventArgs args)
{
var prompt = args.Prompt;
}
protected override async Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender)
{
if (firstRender)
{
var url = NavigationManager.ToAbsoluteUri("AI Prompt Docs.pdf");
FileData = await Http.GetByteArrayAsync(url);
StateHasChanged();
}
}
}
The above code serves to have a base page that loads the PDF document we added in a previous step. You may notice that as part of the tools of the PDFViewer a TelerikPopup has been added, which in turn contains a TelerikAIPrompt inside. This custom tool will allow us to ask questions about the document, which will be answered by the AI model based on a context.
The idea is that when the page loads, the document is divided into chunks so that when the user asks a question, they receive only the most relevant information according to its similarity. There are different strategies to achieve this, but in our example, we will split the text of the document into pieces of 500 characters, plus 100 previous characters and 100 subsequent characters to avoid losing too much context between the chunks. We will do this by defining a JavaScript function as shown below:
<script suppress-error="BL9992">
window.getLoadedDocumentText = async () => {
// 1. Find the PDF Viewer instance
const findViewer = () => {
const instances = TelerikBlazor._instances || {};
for (const [_, instance] of Object.entries(instances)) {
if (instance.element?.classList.contains("k-pdf-viewer")) {
return instance;
}
}
return null;
};
let pdfInstance = findViewer();
// 2. Wait until the viewer is initialized
while (!pdfInstance) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 200));
pdfInstance = findViewer();
}
// 3. Wait until the PDF document has loaded
let pdfDocument = pdfInstance.widget.state.pdfDocument;
while (!pdfDocument) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 200));
pdfDocument = pdfInstance.widget.state.pdfDocument;
}
// 4. Read all the text
let allText = "";
for (let pageNumber = 1; pageNumber <= pdfDocument.numPages; pageNumber++) {
const content = await (await pdfDocument.getPage(pageNumber)).getTextContent();
allText += content.items.map(item => item.str).join("");
}
// 5. Create 500-character chunks with 100-character overlap
const chunkSize = 500;
const overlap = 100;
const step = chunkSize - overlap;
const chunks = [];
for (let start = 0; start < allText.length; start += step) {
chunks.push(allText.slice(start, start + chunkSize));
}
// 6. Return the array of chunks
return chunks;
};
</script>
The JS code returns the list of chunks, which we will retrieve from the OnAfterRenderAsync method once we have read the document:
...
TextInChunks = await jsRuntime.InvokeAsync<string[]>("getLoadedDocumentText");
var allText = string.Join(" --- ", TextInChunks);
var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
PageEmbeddings = TextInChunks.Select(x => KeyValuePair.Create(x, embedder.Embed(x))).ToDictionary(k => k.Key, v => v.Value);
The next step will be to create a method called CallOpenAIApi that will allow queries to the AI model, passing as parameters a systemPrompt and a message, returning only the text of the response. We will use this method to generate a series of initial question proposals for users, as well as to answer their questions about the document information:
private async Task<string> CallOpenAIApi(string systemPrompt, string message)
{
var options = new ChatOptions
{
Instructions = systemPrompt
};
var answer = await ChatClient.GetResponseAsync(message, options);
return answer.Text;
}
Once this method is defined and the embeddings list is created, we will generate a series of question suggestions for the user that will be displayed in the TelerikAIPrompt component as follows:
var questionsJson = await CallOpenAIApi(
@"You are a helpful assistant. Your task is to analyze the provided text and generate 3 short diverse questions.
The questions should be returned in form of a string array in a valid JSON format. Return only the JSON and nothing else without markdown code formatting.
Example output: [""Question 1"", ""Question 2"", ""Question 3""]",
allText);
PromptSuggestions = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize<List<string>>(questionsJson);
PopupRef.Refresh();
StateHasChanged();
On the other hand, to answer the questions that a user may have, we will apply a flow similar to the one we followed in the two previous smart components, that is, convert the question into an embedding, compare the embedding against the dictionary of embeddings, and return the closest elements, as follows:
private async Task<string> AnswerQuestion(string question)
{
var embedder = new LocalEmbedder();
var questionEmbedding = embedder.Embed(question);
var results = LocalEmbedder.FindClosest(questionEmbedding, PageEmbeddings.Select(x => (x.Key, x.Value)), 2);
string prompt = $"You are a helpful assistant. Use the provided context to answer the user question. Context: {string.Join(" --- ", results)}";
var answer = await CallOpenAIApi(prompt, question);
return answer;
}
In the code above, you can notice how the FindClosest method is used to return only the closest items according to the specified quantity. Similarly, we will modify the HandlePromptRequest method to display the response to the user in the TelerikAIPrompt component as shown below:
private async Task HandlePromptRequest(AIPromptPromptRequestEventArgs args)
{
var prompt = args.Prompt;
var answer = await AnswerQuestion(prompt);
args.Output = answer;
}
When running the application with the previous changes, we first see the initial prompt suggestions that have been generated from the document. You can also see that after pressing the Generate button, a response is generated that has used the chunks as a basis to answer the user’s question accurately:
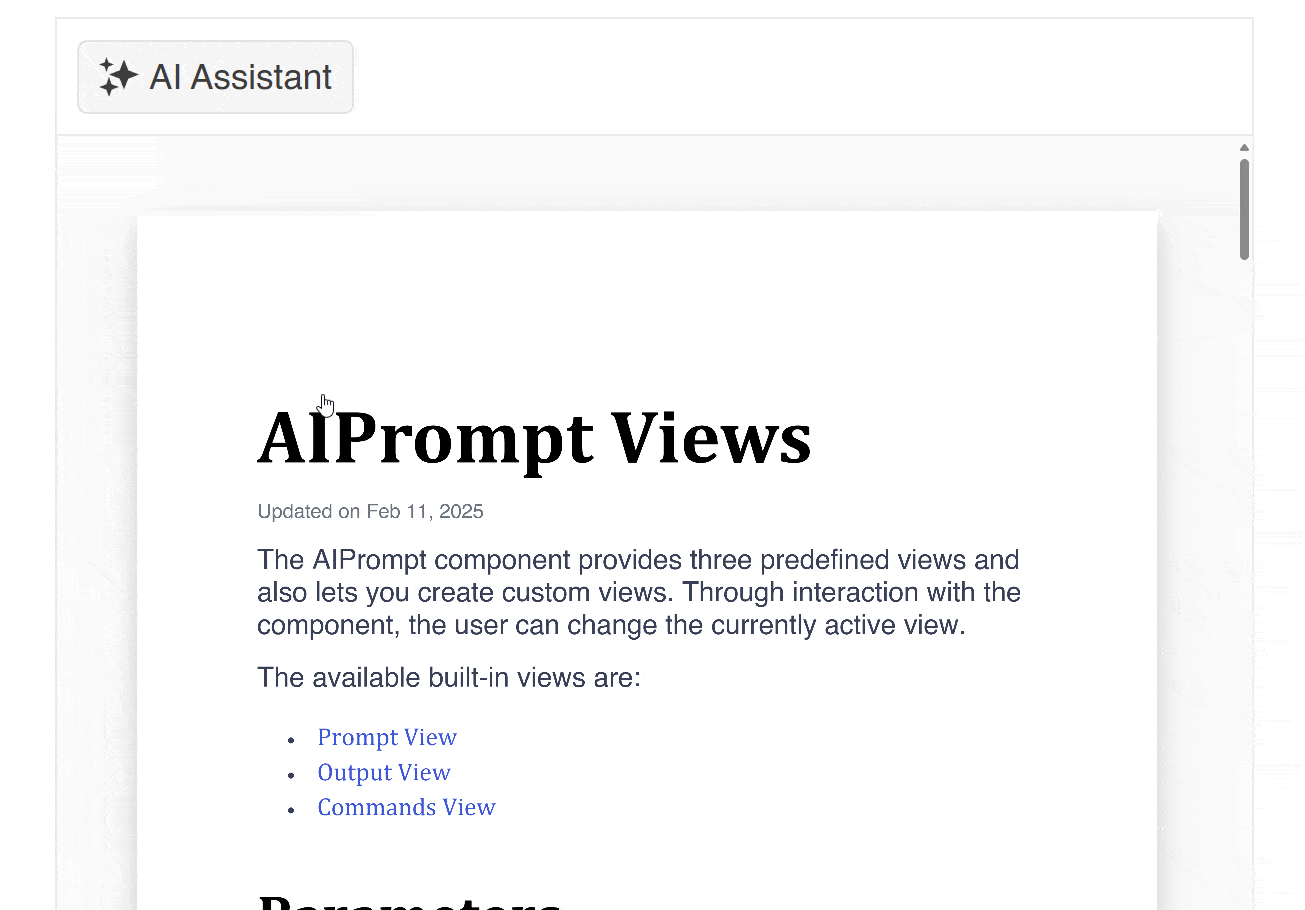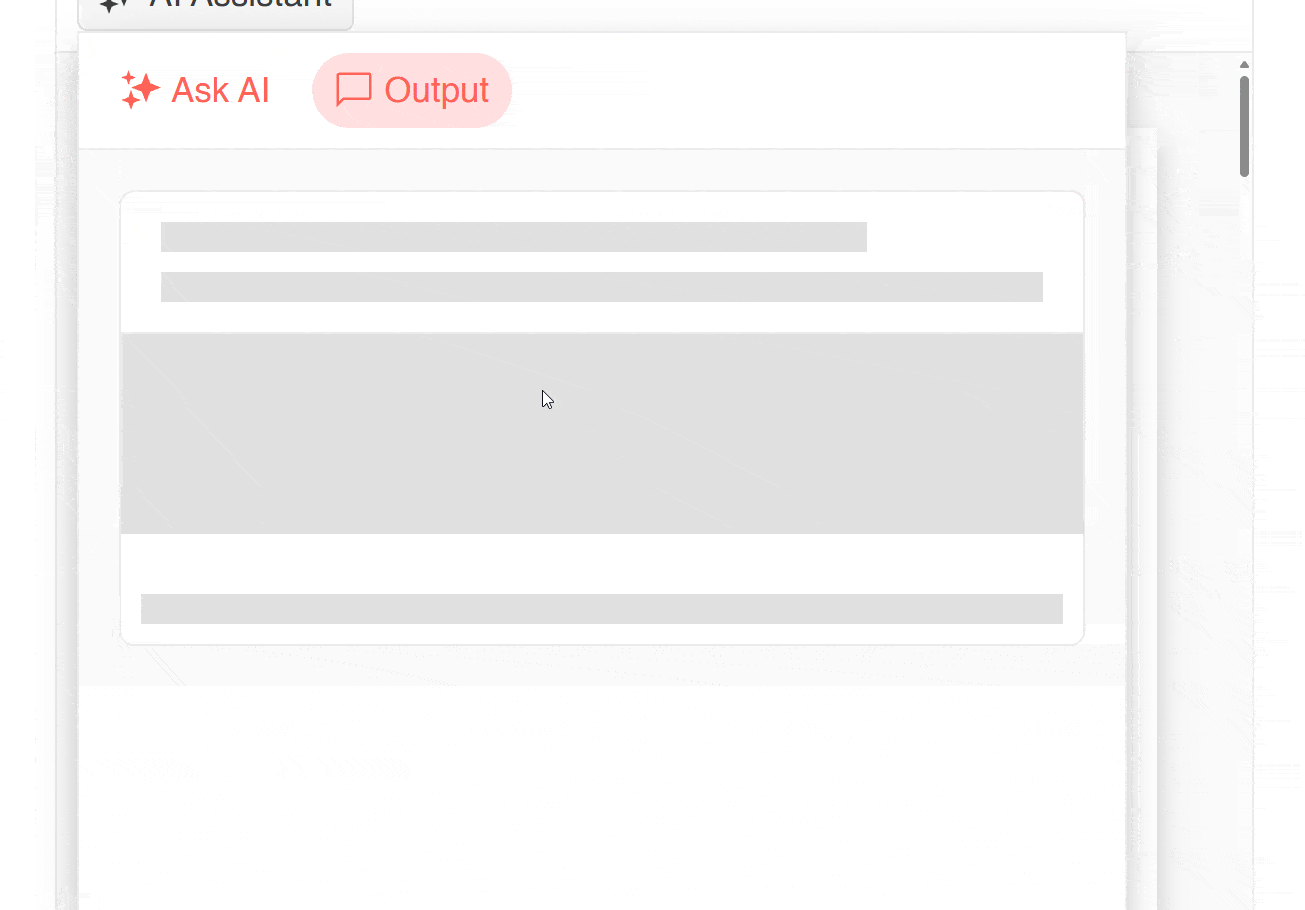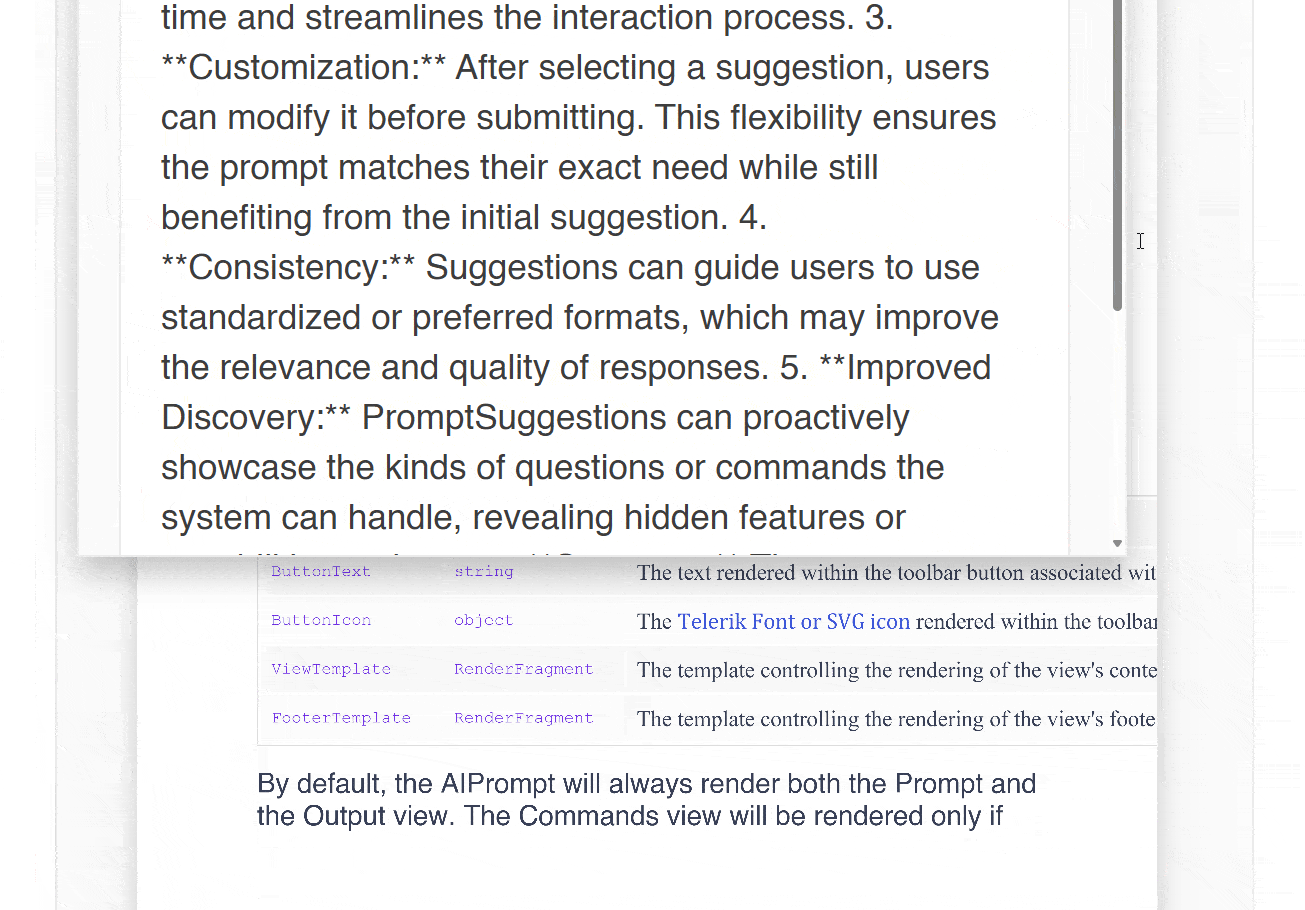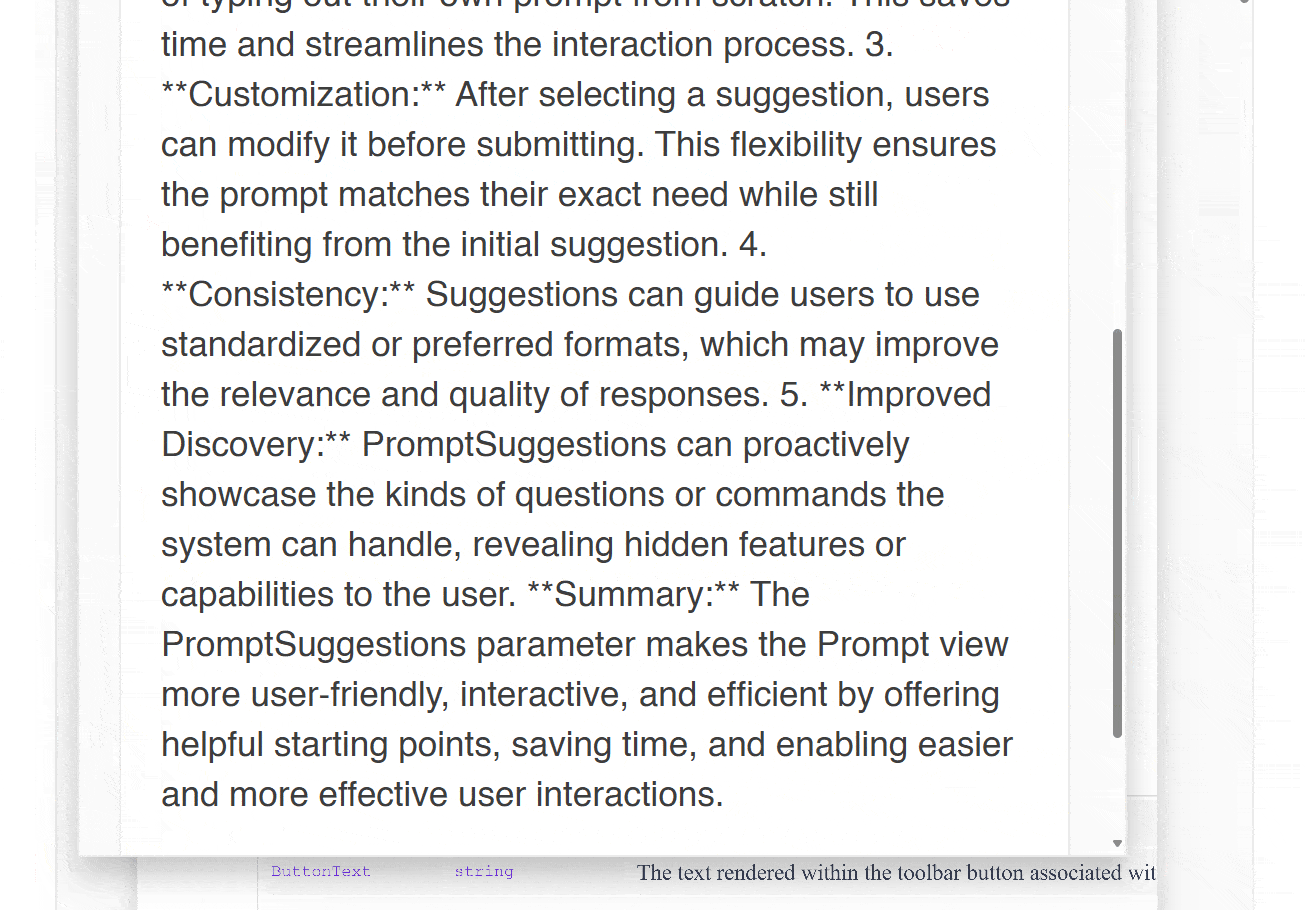
This is how we have implemented Telerik Smart Components in a project from scratch.
Conclusion
Throughout this post, you have learned what Telerik Smart Components are and how to implement them in a Blazor project from scratch. You have also seen the necessary components behind their operation, which has provided you with the tools to integrate these new Smart Components into your own projects, giving your users better experiences through the use of AI.
Ready to try Telerik UI for Blazor? It comes with a free 30-day trial.

Héctor Pérez
Héctor Pérez is a Microsoft MVP with more than 10 years of experience in software development. He is an independent consultant, working with business and government clients to achieve their goals. Additionally, he is an author of books and an instructor at El Camino Dev and Devs School.

