React Basics: How to Use Cookies in React

Summarize with AI:
In this article, we go through some examples of setting and using cookies in a React application for storing and retrieving data, including how to create, read, update and delete cookies, as well as handling cookie consent using a cookie bar.
Cookies are a common way to store and retrieve data on the client side in web applications. Cookies can be used to store information such as user preferences, session data and other data that needs to persist across different sessions or pages.
For a deep-dive into what cookies are and how they compare with the other browser storage mechanisms, be sure to check out the previous article I’ve written titled The Three Browser Storage Mechanisms.
In this article, we’ll go through some examples of setting and using cookies in React, including how to create, read, update and delete cookies, as well as handling cookie consent using a cookie bar.
Setting up Cookies in React
Though cookies can be managed in JavaScript through custom means, using a well-maintained third-party library to manage cookies can help ensure browser compatibility, provide built-in security features, and save us time. Many different popular JavaScript
libraries exist when it comes to handling cookies which include js-cookie, universal-cookie and react-cookie. For this article, we’ll use the js-cookie library, but all the
different libraries will achieve a very similar outcome.
To make use of js-cookie, we first need to install the library using npm or yarn:
npm install js-cookie
Once the library is installed, we can import it into our React component and start using it to interact with cookies. For example, let’s say we want to set a cookie to store a user’s preferred language. We can use the Cookies.set() method provided by the js-cookie library to do this:
import React from 'react';
import Cookies from 'js-cookie';
function App() {
// Set a cookie to store the user's preferred language
const setLanguageCookie = (language) => {
Cookies.set('language', language);
}
return (
/* ... */
);
}
export default App;
In the above example, we define a setLanguageCookie() function that takes a language parameter and uses the Cookies.set() method to set a cookie with the name 'language' and the value of the language parameter.
Reading Cookies
Once a cookie is set, we can read its value using the Cookies.get() method provided by the js-cookie library. We can retrieve a user’s preferred language from the cookie we set earlier
and display it in our React component like the following:
import React from "react";
import Cookies from "js-cookie";
function App() {
// Get the user's preferred language from the cookie
const getLanguageCookie = () => {
return Cookies.get("language");
};
const language = getLanguageCookie();
return (
<div>
<p>Preferred Language: {language}</p>
{/* ... */}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
In the above example, we define a getLanguageCookie() function that uses the Cookies.get() method to retrieve the value of the 'language' cookie. We then
display the retrieved language value in our React component.
Deleting Cookies
To delete a cookie, we can use the Cookies.remove() method provided by the js-cookie library and we can remove the 'language' cookie we’ve set earlier
with the following:
import React from 'react';
import Cookies from 'js-cookie';
function App() {
// Delete the user's preferred language cookie
const clearLanguageCookie = () => {
Cookies.remove('language');
}
// ... other code ...
return (
/* ... */
);
}
export default App;
In the above example, we define a clearLanguageCookie() function that uses the Cookies.remove() method to delete the 'language' cookie.
Handling Cookie Consent with a Cookie Bar
In many web applications, it is sometimes necessary to obtain user consent before setting cookies. A common way to handle this is by displaying a cookie bar that informs the user about the use of cookies and asks for their consent. With React, we can implement this easily with state and conditional rendering.
Here is an example of creating a simple cookie bar component that displays a message and two buttons to allow the user to accept or reject cookies.
import React, { useState } from "react";
import Cookies from "js-cookie";
function CookieBar() {
const [isCookieSet, setCookie] = useState(Cookies.get("cookieConsent"));
// Function to handle accepting cookies
const handleAcceptCookies = () => {
Cookies.set("cookieConsent", true);
setCookie(true);
};
// Function to handle rejecting cookies
const handleRejectCookies = () => {
Cookies.remove("cookieConsent");
setCookie(false);
};
return (
<div>
<div>
<p>
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. Do you accept
cookies?
</p>
<button onClick={handleAcceptCookies}>Accept</button>
<button onClick={handleRejectCookies}>Reject</button>
</div>
<sub>Cookie set: {isCookieSet ? <b>Yes</b> : <b>No</b>}</sub>
</div>
);
}
export default CookieBar;
In the above example, we use the React useState() hook to manage the state of the cookie bar component. The isCookieSet state variable is set to true if
the 'cookieConsent' cookie is present otherwise will have a value of false.
When the user clicks the “Accept” or “Reject” button, the 'cookieConsent' cookie is set or removed with the Cookies.set() or Cookies.remove() methods respectively.
In the Cookies section of our browser developer tools, we’ll be able to see the 'cookieConsent' cookie be added and removed whenever the respective buttons are clicked and the page is subsequently
refreshed.
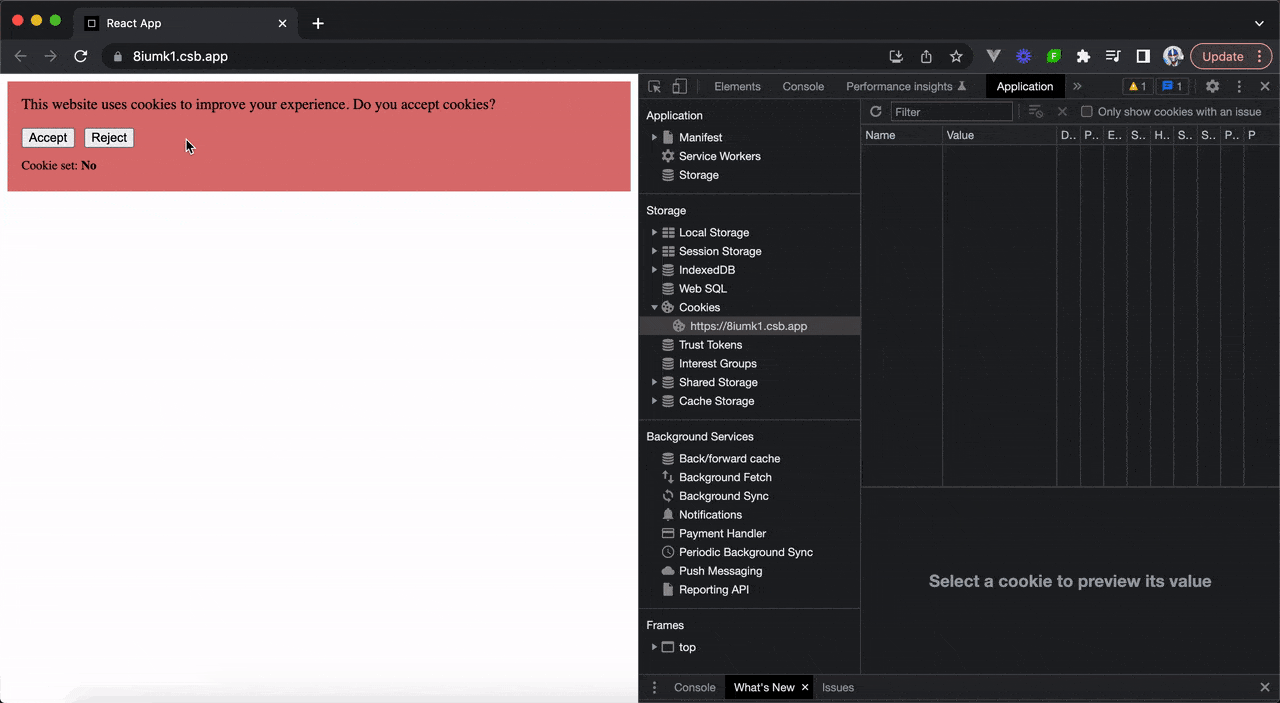
The above example can be viewed in this CodeSandbox.
Wrap-up
In this article, we’ve covered the basics of using cookies in React by learning how to set, read, update and delete cookies using the js-cookie library. We’ve also seen a simple example on how cookie consent
can be handled with a cookie bar component in React.
Cookies are a useful tool for storing and retrieving data on the client side in web applications, but it’s important to handle them properly and obtain user consent when necessary!

Hassan Djirdeh
Hassan is a senior frontend engineer and has helped build large production applications at-scale at organizations like Doordash, Instacart and Shopify. Hassan is also a published author and course instructor where he’s helped thousands of students learn in-depth frontend engineering skills like React, Vue, TypeScript, and GraphQL.

