The Three Browser Storage Mechanisms

Summarize with AI:
Three different storage mechanisms exist for the web browser: localStorage, sessionStorage and cookies. In this article, we’ll explore the differences for each of the three mechanisms that make them more suitable for different types of data and applications.
In November 2022, Ifeoma Imoh posted a great article on all things one needed to know when working with localStorage in JavaScript.
In today’s article, we’ll focus on the comparison between localStorage and other storage mechanisms of the web browser.
There are three different storage mechanisms of the web browser—localStorage, sessionStorage and cookies. All three mechanisms have some differences that make them more suitable for different types of data and applications.
localStorage
localStorage is storage data that is only stored in the browser where:
- Stored data is persistent. This means this data remains in the browser’s memory even if the user refreshes the web page or closes and reopens the browser window.
- Stored data is only accessible through client-side JavaScript and cannot be accessed by the server.
- Stored data is not automatically sent to the server with every HTTP request. This means that the server will not have access to the data unless it is specifically requested.
We can test localStorage right in our browser since localStorage is an object that can be accessed through the browser’s Window interface. The
localStorage object contains the setItem() function that takes two arguments:
- A key, which acts as a unique identifier for the data we intend to store.
- And a value, which is the data itself we want to store.
In the Console tab of our browser’s dev tools, we can run the following command to store the string value of "Hello World!" to the key labeled greeting:
localStorage.setItem("greeting", "Hello World!");
To see what is stored in localStorage, we can use the developer tools in our web browser. For example, in Google Chrome, we can go to the Application tab to view the contents of
localStorage. At this point, we should see a "greeting" : "Hello World!" be shown as data stored as localStorage.
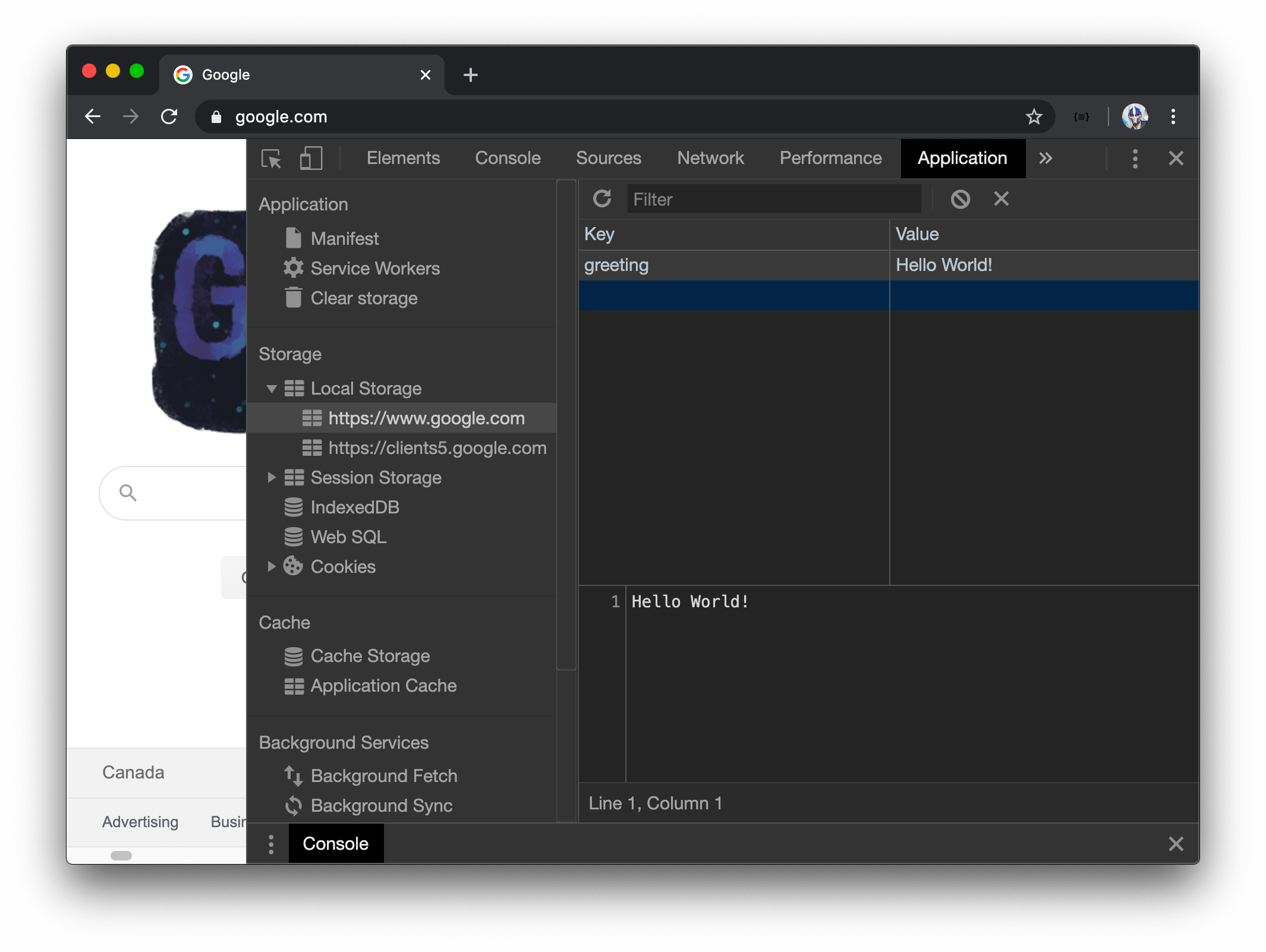
If we were to refresh the web page, close and reopen the tab, close and reopen the browser, or even restart our computer, the data remains! The only way to delete this data is to either clear our browser’s memory or explicitly delete the
localStorage data with the removeItem() or clear() function.
We can use the localStorage.removeItem() function to delete the data stored for a specific key.
localStorage.removeItem("greeting");
And we can use the localStorage.clear() function to delete all localStorage data.
sessionStorage
sessionStorage behaves similarly to localStorage in that the data stored with it is only accessible through client-side JavaScript and is not automatically sent to the server with every
HTTP request. However,
sessionStorage has one key difference: the data stored with it is automatically deleted when the user closes the browser tab or window where the data was stored.
We can test this out in the browser as well. The sessionStorage object has the same functions as the localStorage object so we can use the setItem() function to assign the "Hello World!" string value to the key labeled greeting. We’ll run the following command in the Console of our browser’s
dev tools.
sessionStorage.setItem("greeting", "Hello World!");
Like we’ve seen earlier, we can go to the Application tab of Google Chrome to view the contents of sessionStorage.
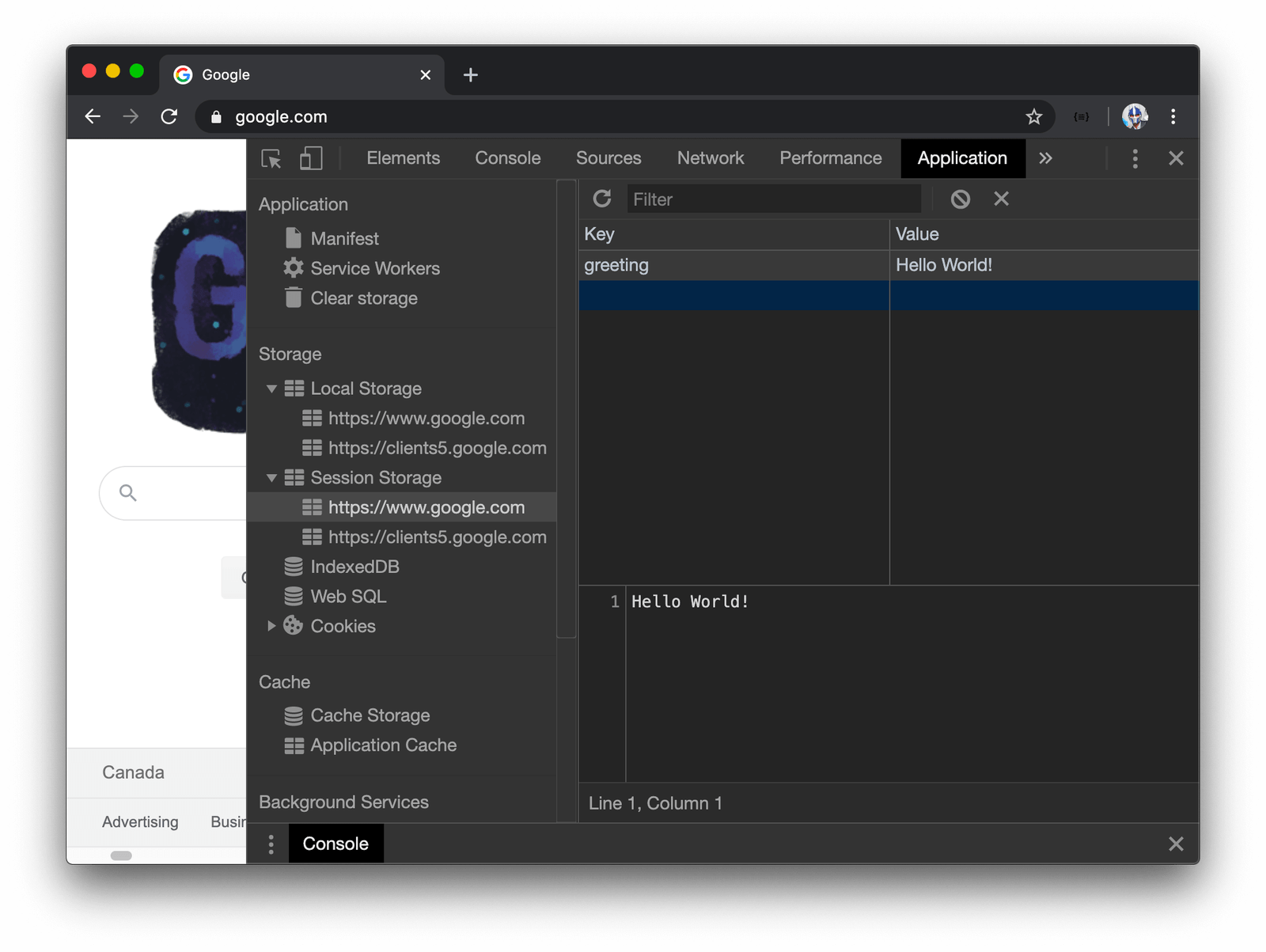
When we refresh the web-page, the data will not be deleted (just like localStorage ). However, by closing and reopening the browser tab or closing and reopening the browser window, the data will be deleted!
Alternatively, like localStorage, data can also be deleted by clearing out the browser’s memory or with the removeItem() and clear() functions:
sessionStorage.removeItem("greeting");
sessionStorage.clear();
Cookies
Cookies are another form of data that can be stored in the browser. Some key properties of cookies include:
- Persistence. The data stored in cookies is persistent, which means it will remain in the browser even if the user refreshes the web page or closes and reopens the browser window.
- Accessibility/Security. Cookies can be marked as
HttpOnlywhich means that they can only be accessed by the server and not by JavaScript running in the browser. This helps to protect the security of the data stored in the cookie. - Automatic transmission. Unlike
localStorageorsessionStorage, the data stored in cookies is automatically sent to the server with every HTTP request.
Cookies, like localStorage, are persistent in memory. If we were to refresh the web-page or close and re-launch the browser window (or tab), the data stored in cookies will not be deleted. However, cookie data
can be deleted if we were to explicitly clear browser memory or the cookie happens to reach its expiration date.
localStorage & sessionStorage Security
Both localStorage and sessionStorage are accessible through JavaScript running in the browser. This means that any data stored in these types of storage, such as authentication
data, is vulnerable to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. In a XSS attack, an attacker can inject client-side scripts, such as JavaScript, into a web app in order to gain access to sensitive information.
There are some steps we can take to prevent XSS attacks.
- We can ensure all links on our website are from a trusted source. This includes not only the URLs of
<a/>tags, but also the URLs of<img/>elements, as attackers can use these to inject malicious code into the web app. - We can escape untrusted data. This is often done automatically when using a modern front-end framework like React.
However, when it comes to storing sensitive data in the browser, cookies are better suited for storing sensitive data than localStorage or sessionStorage.
Cookie Security
Cookies can be marked as HttpOnly and thus can only be accessed by the server and not by JavaScript running in the browser. This make cookies immune to XSS attacks. We can also set a Secure flag to a cookie to guarantee the cookie is only sent over HTTPS. These are some of the reasons why cookies are often used to store sensitive tokens or session data.
However, cookies are vulnerable to a type of attack known as cross-site request forgery (CSRF). In a CSRF attack, an attacker lures a victim to a malicious website or email, which causes the victim’s web browser to perform an unwanted HTTP request to another website where the victim is currently authenticated. This exploit of how the browser handles cookies can allow the attacker to gain access to sensitive information.
To help prevent CSRF attacks, the SameSite flag was introduced for cookies. When this flag is set, cookies are not sent with cross-site requests, which makes it much more difficult for attackers to perform a CSRF
attack.
Some older browsers still don’t support the SameSite flag. For an additional step to countering CSRF, we can include a token (e.g. X-CSRF-TOKEN) with every HTTP request. This
helps to ensure that the request is being made by the intended user and not an attacker. By using both the SameSite flag and a token, you can help to protect your web app from CSRF attacks and keep your
users’ data safe.
Wrap-up
In this article, we compared the three mechanisms available to us for storing data in the browser’s memory: localStorage, sessionStorage and cookies. We’ve seen how
each mechanism has some differences that make it more suitable for different types of data and applications.
For example, localStorage data is persistent, whereas sessionStorage data is automatically deleted when the user closes the browser tab or window where the data was stored. Lastly,
cookies are unique in that they are automatically sent to the server with every HTTP request and can be marked as HttpOnly to prevent JavaScript from accessing them.

Hassan Djirdeh
Hassan is a senior frontend engineer and has helped build large production applications at-scale at organizations like Doordash, Instacart and Shopify. Hassan is also a published author and course instructor where he’s helped thousands of students learn in-depth frontend engineering skills like React, Vue, TypeScript, and GraphQL.

