Getting Started with KendoReact Localization

Summarize with AI:
Creating a React app for a global audience should include adapting the content to local contexts. See how KendoReact Localization can help.
Building applications for a global audience means more than just translating text; it also involves adapting content to local contexts. It consists of adapting layouts, date formats and number conventions to create a native experience for users, regardless of their location. This process is known as localization, and it plays a crucial role in creating inclusive and user-friendly software.
In this article, we’ll explore the Progress KendoReact Localization package and see how it makes internationalization straightforward by providing message translation capabilities and right-to-left (RTL) support for your React applications.
The KendoReact Localization package is part of KendoReact, an enterprise-grade UI library with over 120 components for building polished, performant apps.
KendoReact Localization
The KendoReact Localization package handles two main aspects of internationalization: translating component messages and supporting right-to-left text direction. This means we can create applications that work naturally for users, whether they’re reading English, Arabic or any other language our application needs to support.
Let’s dive into an example to see how we can make a React Grid component fluent in multiple languages.
Translating Component Messages
First, we need to provide the translation messages for the languages we want to support. The KendoReact library makes this easy with the loadMessages function, which associates a set of messages with a specific locale.
These messages are simple key-value pairs. For Spanish and Arabic, the message files would look like this:
// messages-es.js
export default {
'kendo.grid.noRecords': 'No hay registros disponibles',
// ...
};
// messages-ar.js
export default {
'kendo.grid.noRecords': 'لا توجد سجلات متاحة',
// ...
};
In the example below, we’ll set up a Grid that can switch between English, Spanish and Arabic. We’ll use a React DropDownList to let the user select a language, and the Grid will update its content and internal messages (like pagination controls) accordingly.
import * as React from 'react';
import { Grid, GridColumn as Column } from '@progress/kendo-react-grid';
import {
IntlProvider,
LocalizationProvider,
loadMessages,
} from '@progress/kendo-react-intl';
import { DropDownList } from '@progress/kendo-react-dropdowns';
// Mock message files for Spanish and Arabic
import esMessages from './messages-es';
import arMessages from './messages-ar';
// Load the messages for each locale
loadMessages(esMessages, 'es-ES');
loadMessages(arMessages, 'ar-SA');
// Custom column titles for different languages
const columnTitles = {
'en-US': {
ProductID: 'ID',
ProductName: 'Product Name',
UnitPrice: 'Unit Price',
},
'es-ES': {
ProductID: 'ID',
ProductName: 'Nombre del producto',
UnitPrice: 'Precio unitario',
},
'ar-SA': {
ProductID: 'معرف المنتج',
ProductName: 'اسم المنتج',
UnitPrice: 'سعر الوحدة',
},
};
const App = () => {
const [locale, setLocale] = React.useState('en-US');
const handleLocaleChange = (event) => {
setLocale(event.target.value.value);
};
const languageOptions = [
{ text: 'English', value: 'en-US' },
{ text: 'Español', value: 'es-ES' },
{ text: 'العربية', value: 'ar-SA' },
];
const titles = columnTitles[locale] || columnTitles['en-US'];
return (
<div>
<div className="example-config">
<p>Select Language:</p>
<DropDownList
data={languageOptions}
textField="text"
dataItemKey="value"
value={languageOptions.find((l) => l.value === locale)}
onChange={handleLocaleChange}
/>
</div>
<LocalizationProvider language={locale}>
<IntlProvider locale={locale}>
<Grid style={{ height: '420px' }} data={[]}>
<Column
field="ProductID"
title={titles.ProductID}
filterable={false}
width="100px"
/>
<Column field="ProductName" title={titles.ProductName} />
<Column
field="UnitPrice"
title={titles.UnitPrice}
filter="numeric"
format="{0:c}"
/>
</Grid>
</IntlProvider>
</LocalizationProvider>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
In this code, we first import loadMessages, LocalizationProvider and IntlProvider, and we load our Spanish and Arabic message files. The locale is stored in React state, which is updated by the DropDownList. The Grid and its Column components are wrapped in LocalizationProvider and IntlProvider, which pass the selected locale down.
This automatically translates built-in messages, like those in the filter menus or the pager. For custom text, like our column titles, we use a simple columnTitles object to look up the correct translation based on the current locale.
With this, we get a language selector that allows us to switch between English, Spanish and Arabic.
Right-to-Left (RTL) Support
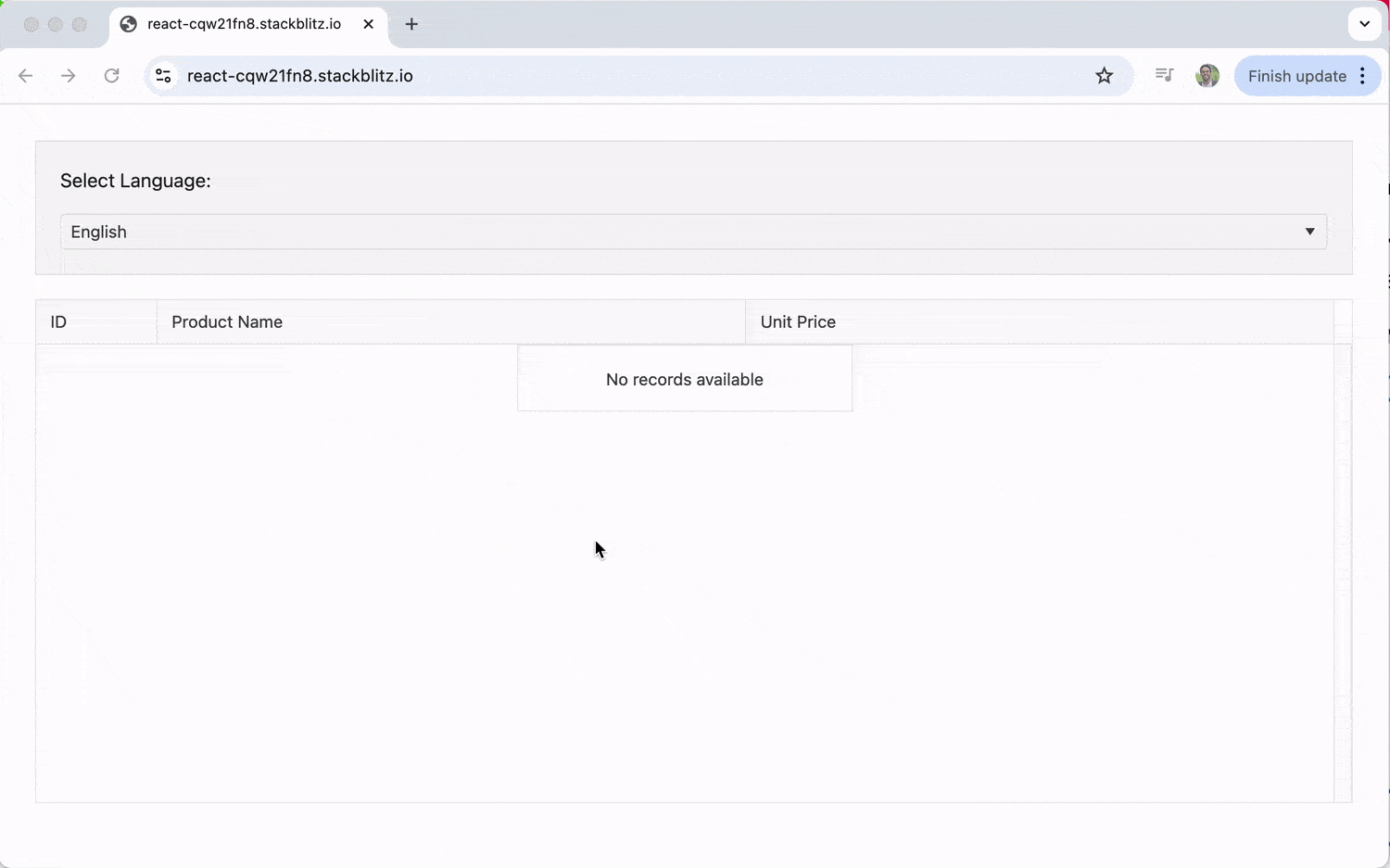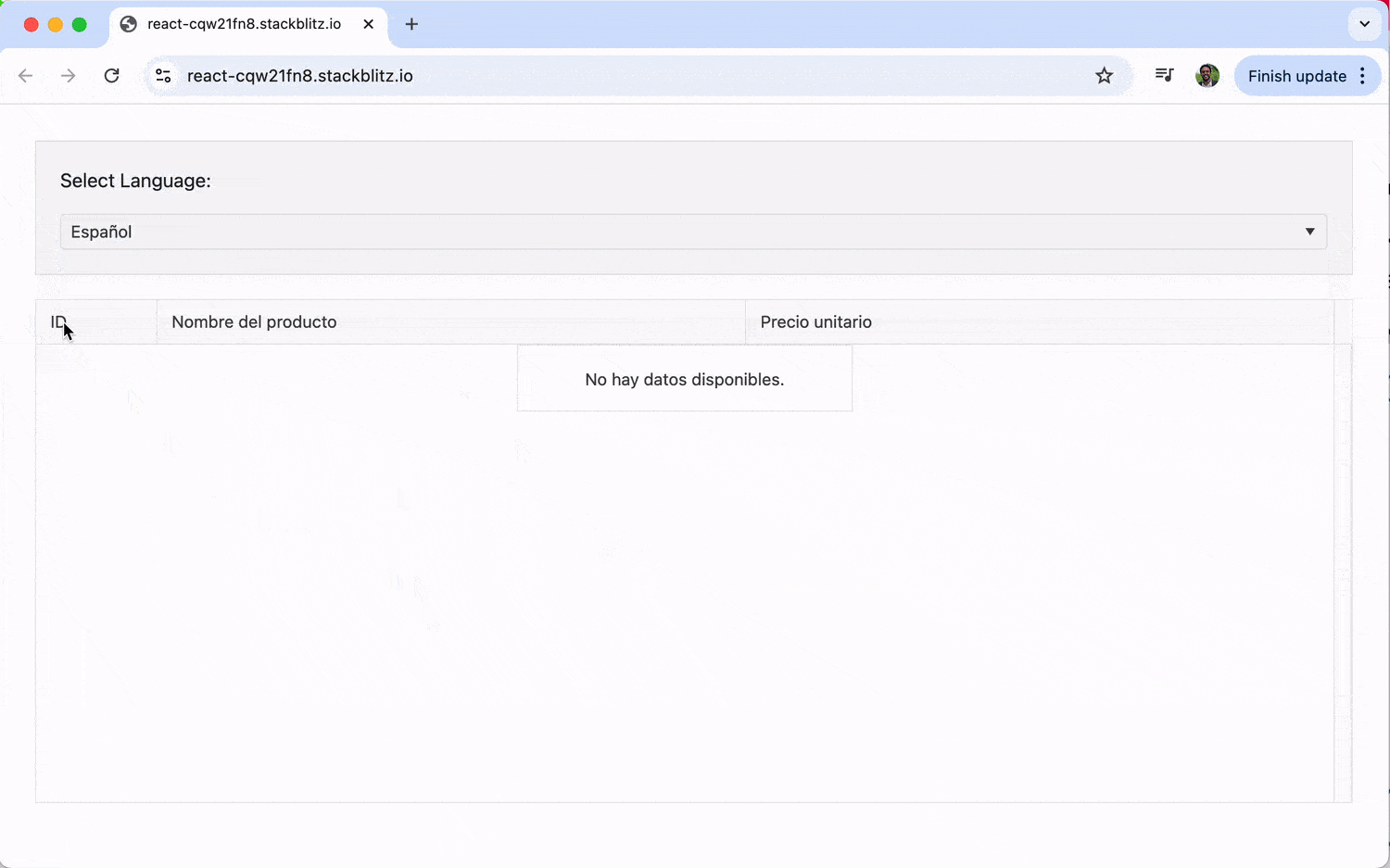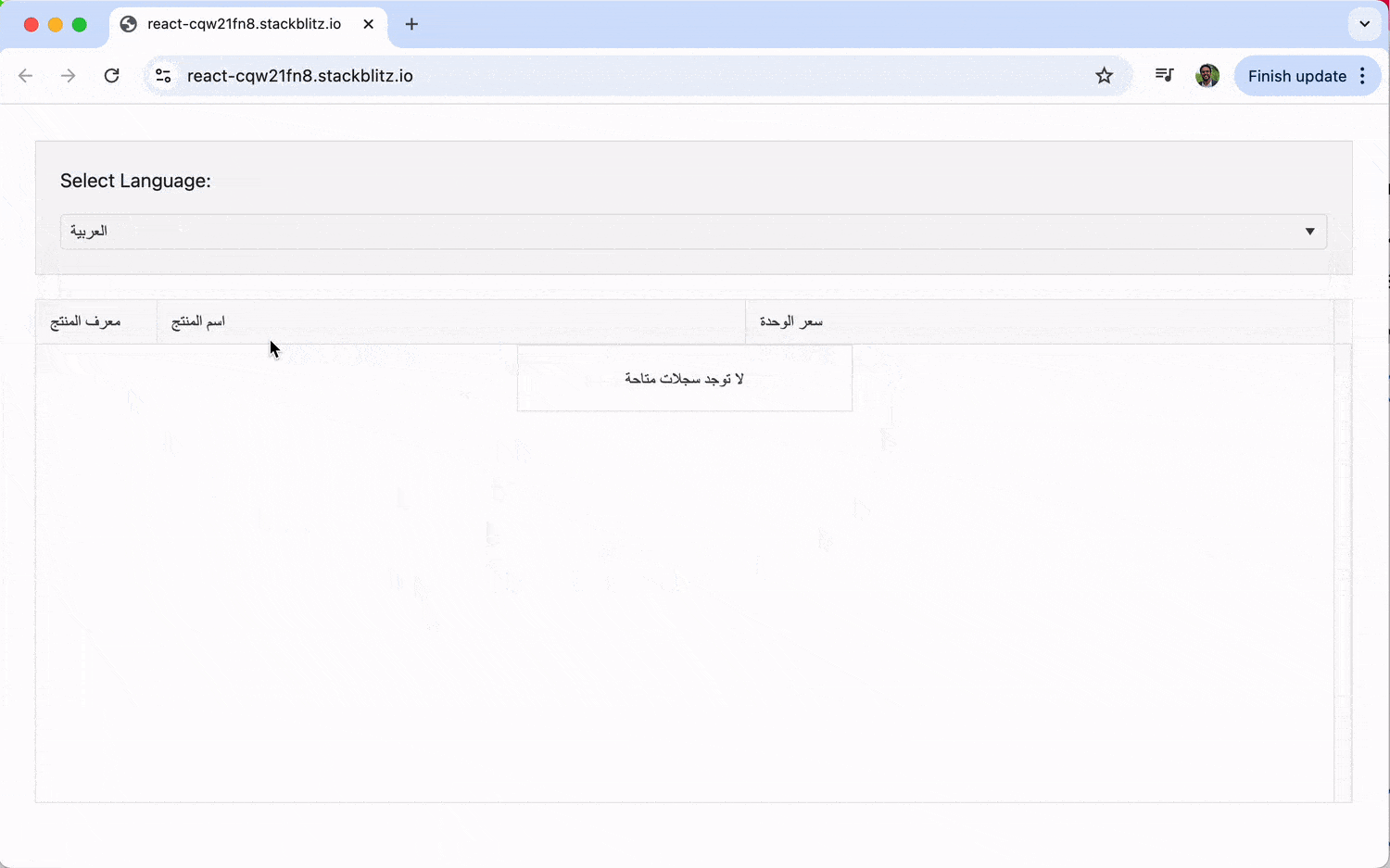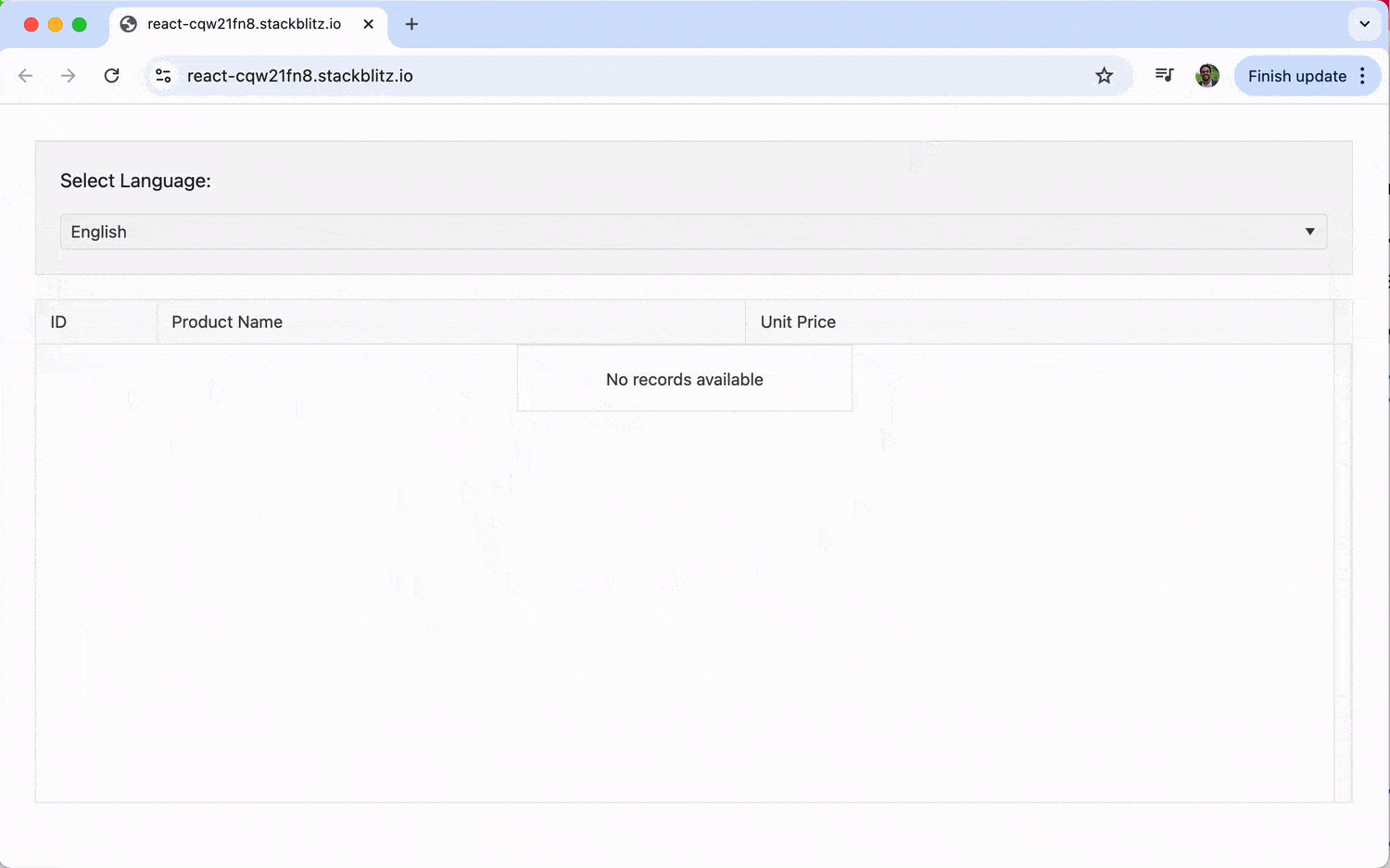
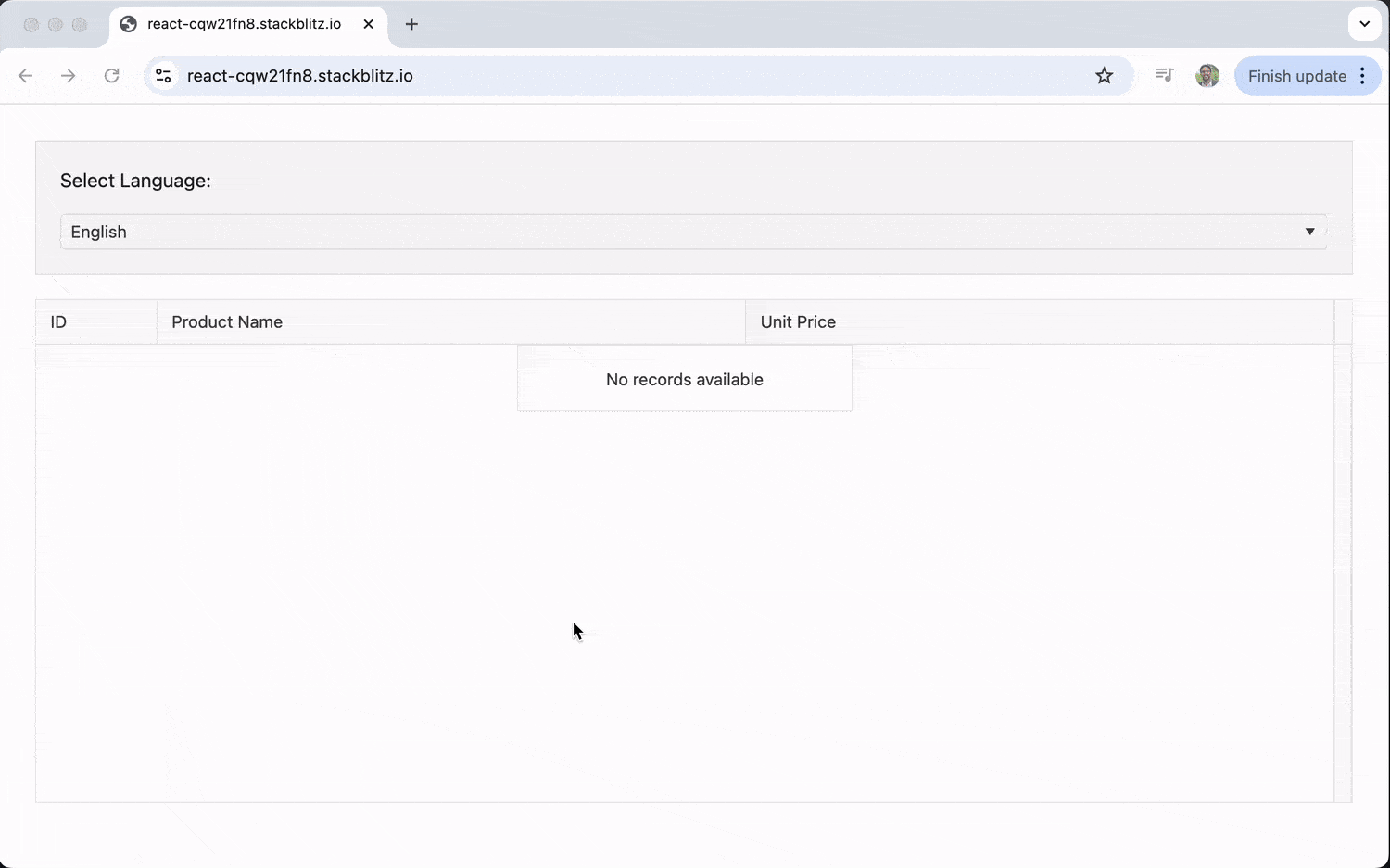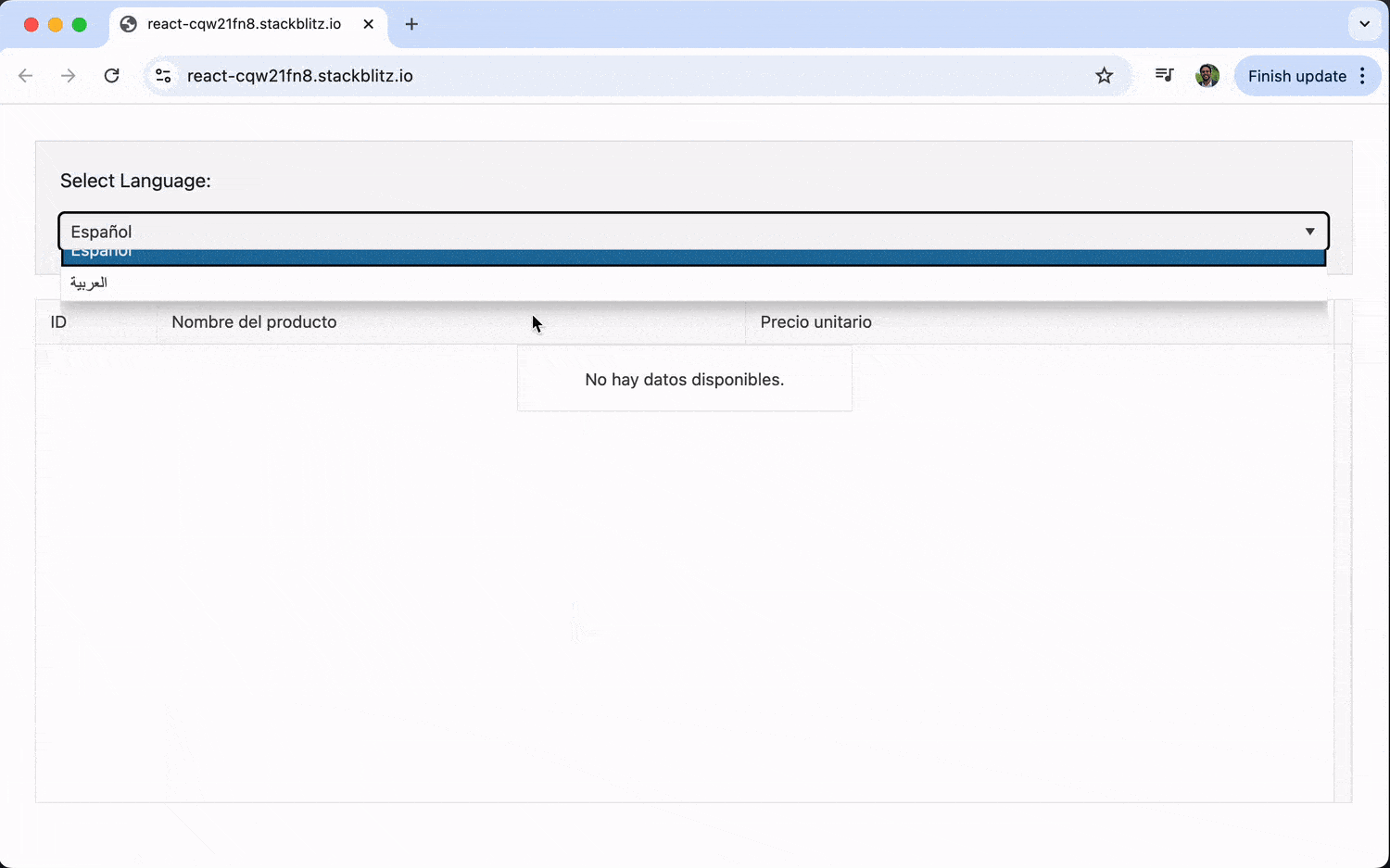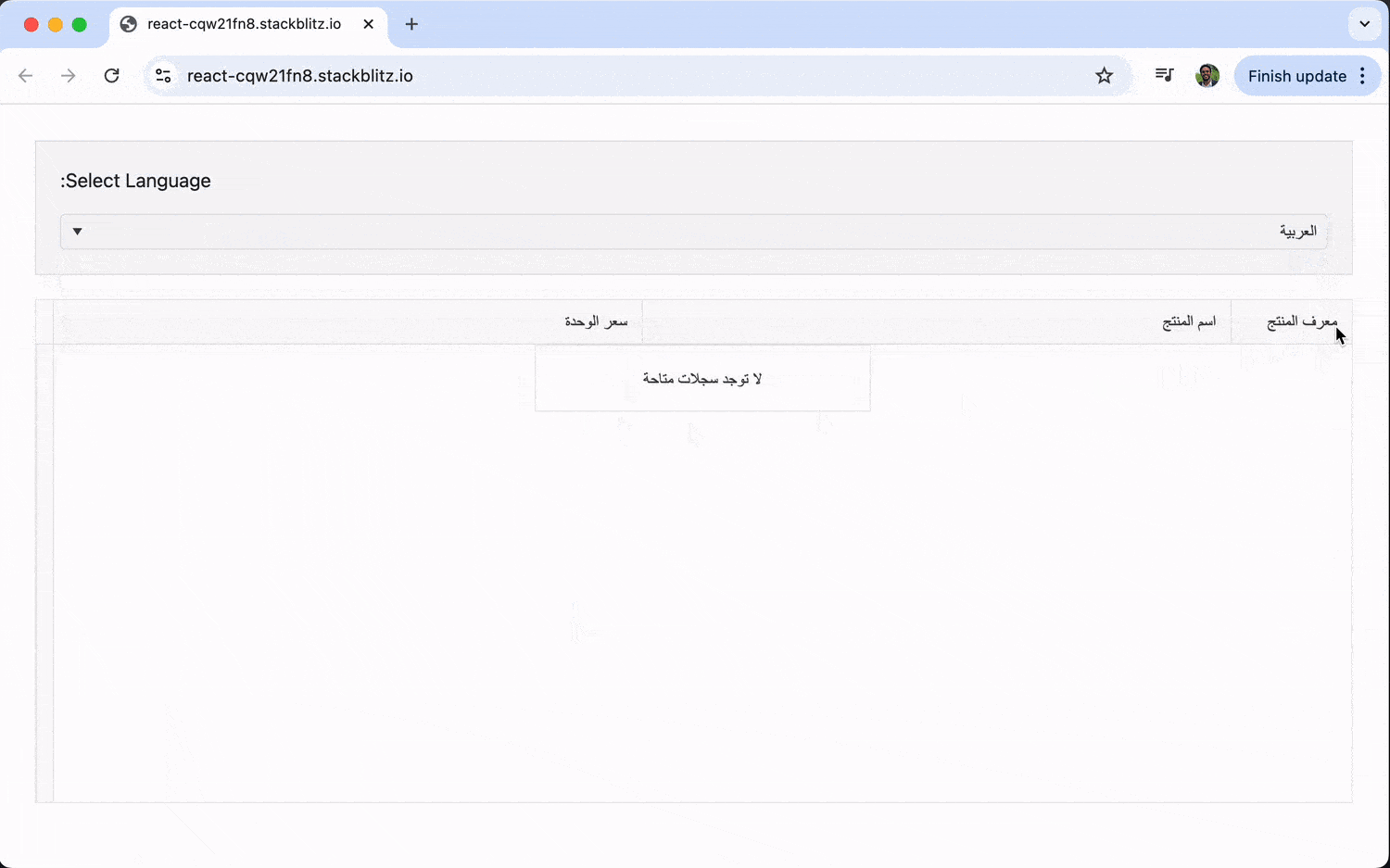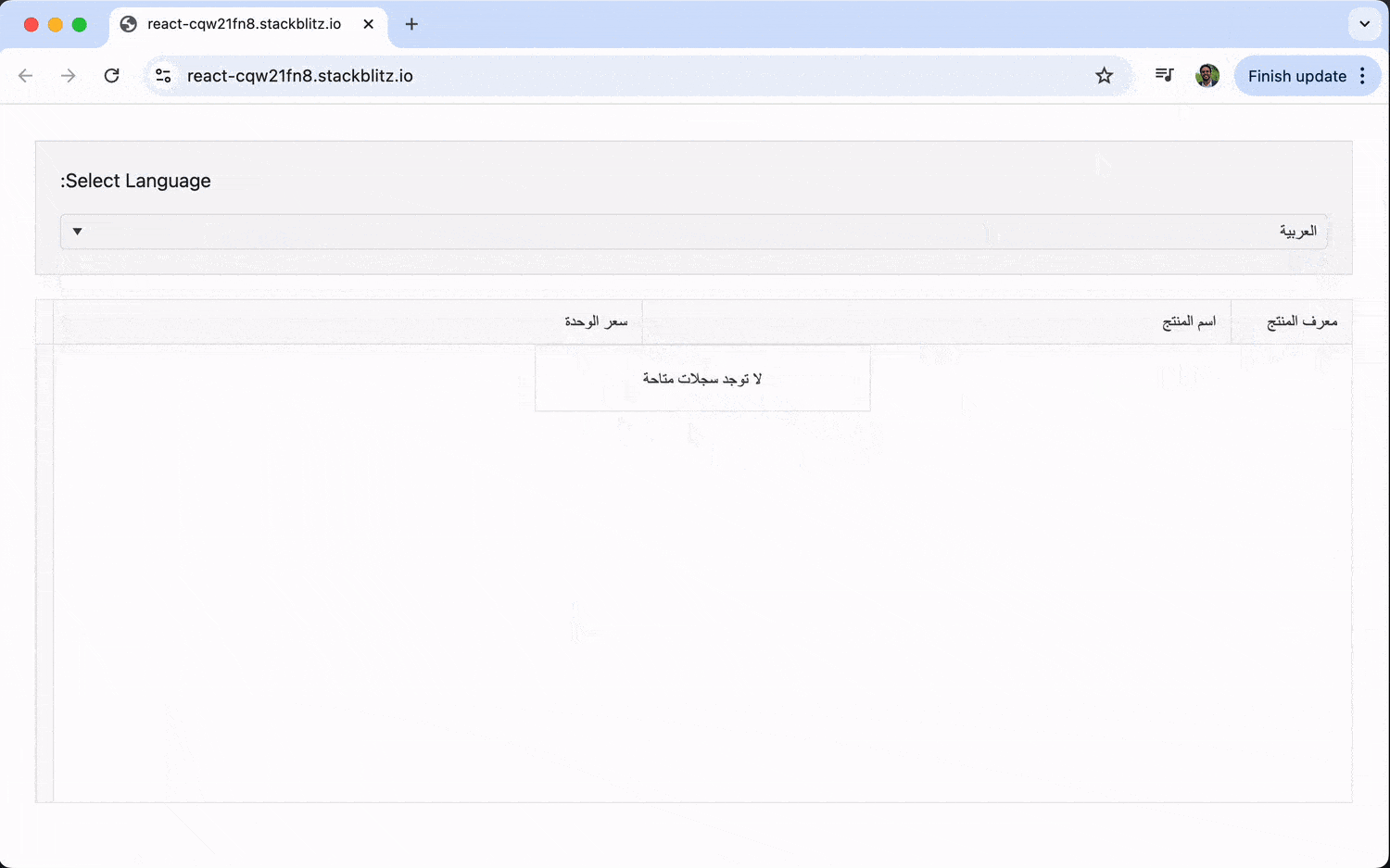
Some languages, such as Arabic, are read from right to left. A proper localization strategy must also adapt the application’s layout to accommodate these users. KendoReact components have built-in RTL support, which can be enabled by adding a dir="rtl" attribute to a parent element.
Let’s extend our previous example. When the user selects Arabic ('ar-SA'), we’ll not only translate the text but also flip the UI into RTL mode.
import * as React from 'react';
import { Grid, GridColumn as Column } from '@progress/kendo-react-grid';
import {
IntlProvider,
LocalizationProvider,
loadMessages,
} from '@progress/kendo-react-intl';
import { DropDownList } from '@progress/kendo-react-dropdowns';
// Message files and column titles would be defined here as in the previous example...
import esMessages from './messages-es';
import arMessages from './messages-ar';
loadMessages(esMessages, 'es-ES');
loadMessages(arMessages, 'ar-SA');
const columnTitles = {
'en-US': {
ProductID: 'ID',
ProductName: 'Product Name',
UnitPrice: 'Unit Price',
},
'es-ES': {
ProductID: 'ID',
ProductName: 'Nombre del producto',
UnitPrice: 'Precio unitario',
},
'ar-SA': {
ProductID: 'معرف المنتج',
ProductName: 'اسم المنتج',
UnitPrice: 'سعر الوحدة',
},
};
const App = () => {
const [locale, setLocale] = React.useState('en-US');
const isRtl = locale === 'ar-SA';
const handleLocaleChange = (event) => {
setLocale(event.target.value.value);
};
const languageOptions = [
{ text: 'English', value: 'en-US' },
{ text: 'Español', value: 'es-ES' },
{ text: 'العربية', value: 'ar-SA' },
];
const titles = columnTitles[locale] || columnTitles['en-US'];
return (
<div dir={isRtl ? 'rtl' : 'ltr'}>
<div className="example-config">
<p>Select Language:</p>
<DropDownList
data={languageOptions}
textField="text"
dataItemKey="value"
value={languageOptions.find((l) => l.value === locale)}
onChange={handleLocaleChange}
/>
</div>
<LocalizationProvider language={locale}>
<IntlProvider locale={locale}>
<Grid style={{ height: '420px' }} data={[]}>
<Column
field="ProductID"
title={titles.ProductID}
filterable={false}
width="100px"
/>
<Column field="ProductName" title={titles.ProductName} />
<Column
field="UnitPrice"
title={titles.UnitPrice}
filter="numeric"
format="{0:c}"
/>
</Grid>
</IntlProvider>
</LocalizationProvider>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
The key change here is the dir attribute on the root div. We check if the current locale is 'ar-SA' and set dir to 'rtl' if it is. This simple change is all that’s needed for KendoReact components to reverse their layout, so column order, text alignment and component controls are all correctly displayed for right-to-left readers.
Wrap-up
The KendoReact Localization package offers a comprehensive and user-friendly solution for adapting your applications to a global audience. By combining message translation with seamless right-to-left support, we can create interfaces that feel natural and intuitive to users from any region.
For more details on the KendoReact Localization package, including additional configuration options and the complete list of available message keys, be sure to check out the official documentation.
And if you want to try it yourself, download the free 30-day trial.

Hassan Djirdeh
Hassan is a senior frontend engineer and has helped build large production applications at-scale at organizations like Doordash, Instacart and Shopify. Hassan is also a published author and course instructor where he’s helped thousands of students learn in-depth frontend engineering skills like React, Vue, TypeScript, and GraphQL.

