Declarative Data Source
The ASP.NET 2.x/3.x allows declarative data binding, which eliminates the coding necessary for connecting a control to its underlying data source. RadGrid employs this new way of accessing data, so that its data binding can be accomplished in a completely declarative manner using data source controls.
Declarative data source controls expose data from a back-end store (SQL database, middle-tier business object, XML file, XML Web Service) to data-bound UI control on a page. Data Source controls also provide new capabilities such as sorting, paging, caching, updating, inserting, and deleting data, which UI controls can automatically use of without any additional code.
Data Source Controls
Data source controls have no rendering, but instead represent a particular backend data store, for example a database, business object, XML file, or XML Web Service. ASP.NET includes the following server controls out-of-the-box, which are all supported by RadGrid:
- SqlDataSource - Enables binding to a SQL database represented by an ADO.NET provider, such as Microsoft™ SQL Server, OLEDB, ODBC, or Oracle.
SqlDataSource is intended to replace the ADO.NET code you would normally write in a page to create a connection and command to query a database. Because the data queries are specified directly as properties of the data source control, this is sometimes called a two-tier model. The data queries are still maintained in page code.
- ObjectDataSource - Enables binding to a middle-tier object such as a data access layer or business component.
The ObjectDataSource control object model is similar to the SqlDataSource control. Instead of a ConnectionString property, ObjectDataSource exposes a TypeName property that specifies an object type (class name) to instantiate for performing data operations. Similar to the command properties of SqlDataSource, the ObjectDataSource control supports properties such as SelectMethod, UpdateMethod, InsertMethod, and DeleteMethod for specifying methods of the associated type to call to perform these data operations.
-
AccessDataSource - Enables binding to a Microsoft™ Access (Jet) database.
-
SiteMapSource - Enables binding to the hierarchy exposed by an ASP.NET 2.0 site navigation provider.
The SiteMapDataSource control is associated to a data-bound control through the control's DataSourceID property. For general information on site navigation in ASP.NET, refer to the SiteMap topic of this manual.
- XmlDataSource - Enables binding to an XML file or document.
XmlDataSource supports a DataFile property for specifying the path to an XML data file to be used as input. You may also specify a TranformFile property to apply an XSLT transformation to the data and an XPath property for specifying a subset of nodes to expose from the data source.
- LinqDataSource- Enables binding to an object or database using LINQ (Language Integrated Query).
LinqDataSourcesupports a ContextTypeName property for specifying the object that encapsulates the data, with the TableName property to specify the field that returns the data collection.
- ObjectContainerDataSource- Enables binding to an object with event-driven support for edits.
ObjectContainerDataSource supports an Instance property for specifying the object that supplies the data. Events are raised for the SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE actions.
Choosing the DataSource control
The easiest way to set the DataSource control in VS.NET 2005 is to use the grid's Smart Tag. Click to expand the "Choose Data Source" drop-down and select the Data Source control.
If there is no Data Source control, you need to create a new one. Choose the
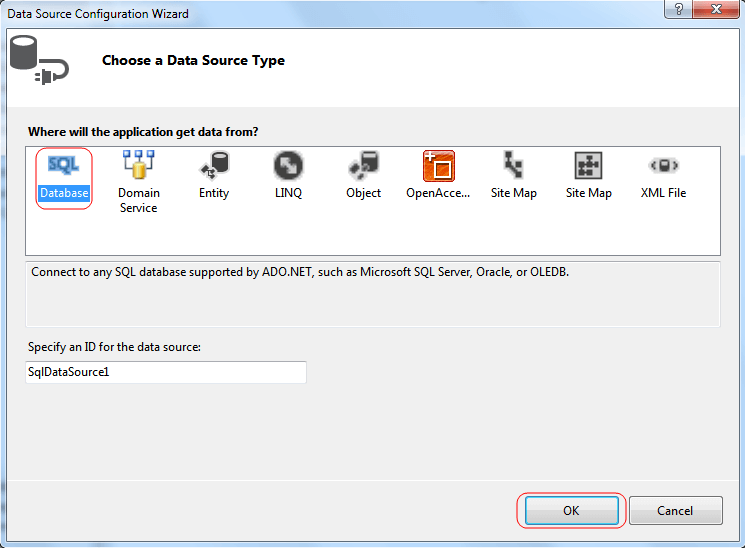
After you choose the Data Source control, your control is automatically bound to the data source.
The Smart Tags for each Data Source control let you easily configure the Data Source (e.g. SQL connection, query string, etc).