Introducing RSC Mode in KendoReact Grid

Summarize with AI:
RSC mode in the KendoReact Data Grid lets you build high-performance React applications by moving data-intensive operations to the server.
The landscape of React development has evolved with the introduction of React Server Components (RSCs) in React 19. As we’ve explored in previous discussions (RSC, SSR and CSR—OMG! and What’s New in React 19), RSCs offer a powerful paradigm for building performant, scalable applications by shifting computation to the server.
In this article, we’ll explore what React Server Components are and how the new Progress KendoReact Grid RSC mode takes advantage of them. We’ll walk through some of the key RSC-powered features now supported in the KendoReact Grid, such as server-side data operations and server actions.
KendoReact Data Grid
The React Data Grid from Progress KendoReact is a feature-rich component designed to handle and present large amounts of data. It comes packed with built-in functionalities like sorting, filtering, grouping and paging, which are essential for any modern data-driven grid user experience.
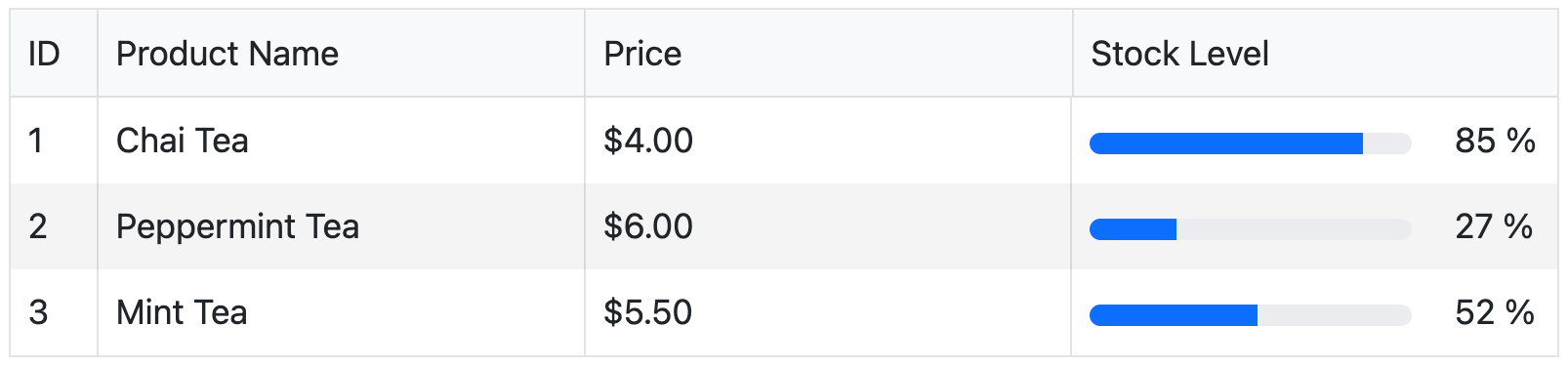
Here’s a quick look at a basic implementation of the component:
import * as React from "react";
import { Grid, GridColumn } from "@progress/kendo-react-grid";
import { ProgressBar } from "@progress/kendo-react-progressbars";
const ProgressCell = (props) => {
const progress = props.dataItem[props.field];
if (props.rowType === "groupHeader") {
return;
}
return (
<td {...props.tdProps}>
<ProgressBar
style={{
width: "150px",
height: "10px",
marginRight: "20px",
}}
value={progress}
labelVisible={false}
/>
{progress} %<span> </span>
</td>
);
};
const App = () => {
const data = [
{
ProductID: 1,
ProductName: "Chai Tea",
UnitPrice: 4.0,
UnitsInStock: 85,
},
{
ProductID: 2,
ProductName: "Peppermint Tea",
UnitPrice: 6.0,
UnitsInStock: 27,
},
{
ProductID: 3,
ProductName: "Mint Tea",
UnitPrice: 5.5,
UnitsInStock: 52,
},
];
return (
<Grid data={data}>
<GridColumn field="ProductID" title="ID" width="40px" />
<GridColumn field="ProductName" title="Product Name" />
<GridColumn field="UnitPrice" title="Price" format="{0:c2}" />
<GridColumn
field="UnitsInStock"
title="Stock Level"
cell={ProgressCell}
/>
</Grid>
);
};
export default App;
In the above code example, we’ve created a basic grid with custom cell rendering for the stock level column using a progress bar component to visually represent the data.
The core features of the KendoReact Data Grid component are available as part of KendoReact Free, the free tier of the enterprise-grade KendoReact component library that includes 50+ React UI components and additional design/UI customization tools.
React Server Components (RSC)
Before we dive into the new KendoReact Grid RSC mode, let’s have a quick refresher on what React Server Components are. Introduced and stabilized in React 19, RSCs allow developers to create stateless React components that run exclusively on the server.
Because these components execute in a server environment, they can access an app’s data layer (like a database or microservice) directly, without needing to fetch data through a separate API endpoint. This fundamentally changes how we think about data fetching in React applications.
import db from "./database";
// A React Server Component
async function BlogPost({ postId }) {
// Fetch data directly from the database on the server
const post = await db.posts.get(postId);
return (
<div>
<h2>{post.title}</h2>
<p>{post.content}</p>
</div>
);
}
As we can see in the simple example above, the BlogPost component fetches its data directly within the component itself. This reduces the amount of JavaScript shipped to the client, leading to faster initial page loads and improved performance.
KendoReact Data Grid RSC Mode
The new RSC mode in the KendoReact Grid is a feature that leverages the power of React Server Components to offload data processing to the server.
By running on the server, KendoReact Grid in RSC mode reduces the client-side bundle size, as the JavaScript for data operations doesn’t need to be sent to the browser. This is ideal for content-heavy applications where initial load time and SEO are critical.
Server-Side Data Operations
One of the more powerful features of the RSC mode is the ability to handle data operations like paging, sorting and filtering all on the server. In a traditional client-side grid, all data is sent to the client, which then performs these operations. With RSC mode, the Grid only needs to concern itself with the data necessary for the client.
State management in RSCs is stateless. For the Grid, this means state changes from data operations are managed on the server, often using cookies to persist the state between requests.
Here’s how we might handle a data state change event on the server:
import { Grid, GridColumn } from "@progress/kendo-react-grid";
import { cookies } from "next/headers"; // example with Next.js App Router
import products from "products.json";
const GRID_STATE_COOKIE = "kendoreact-grid-rsc-state";
const getState = () => {
const cookie = cookies().get(GRID_STATE_COOKIE);
return JSON.parse(cookie?.value);
};
const saveState = (state) => {
cookies().set(GRID_STATE_COOKIE, JSON.stringify(state));
};
const onDataStateChange = async (event) => {
"use server";
saveState(event.dataState);
};
export default async function MyGridPage() {
const data = products;
const dataState = getState();
return (
<Grid
data={data}
onDataStateChange={onDataStateChange}
dataItemKey={"ProductID"}
pageable={true}
sortable={true}
filterable={true}
>
<GridColumn field="ProductID" title="ID" />
<GridColumn field="ProductName" title="Product Name" />
</Grid>
);
}
In the above example, the onDataStateChange event handler is a Server Action (note the 'use server' directive). It saves the Grid’s current state (page, sort order, etc.) to a cookie. When the page rerenders, it reads this state and applies it to the data.
Server Actions
As we’ve seen above, the RSC architecture introduces Server Actions, which are functions that can be passed from server-rendered components to client components and executed on the server.
In the KendoReact Grid, event handlers like onFilterChange, onSortChange and onItemChange can be defined as async functions with the 'use server' directive. This allows us to execute custom server-side logic in response to user interactions in the Grid without a full page reload.
const onSelectionChange = async (event) => {
"use server";
// Custom server logic, e.g., log the selection or update a database
console.log("Selected IDs:", event.dataItem.ProductID);
// Persist the selection state
saveSelectionState(event.select);
};
// ... inside the component
<Grid
onSelectionChange={onSelectionChange}
selectable={true}
// ... other props
/>;
In the above code example, the onSelectionChange function is a Server Action that runs on the server when a user selects a grid row. This enables us to securely handle the interaction on the server (for example, by logging the selected data or updating a database) while also persisting the selection state so the UI remains consistent across requests.
Hybrid Templates: Server and Client
The KendoReact Grid customization capabilities extend into RSC mode with a flexible, hybrid approach to templates. Templates allow us to decide whether a custom cell should be rendered entirely on the server for maximum performance or be hydrated on the client to allow for interactivity.
Server Templates
When performance is important and the content is static, we can use server templates. These are components defined directly within our server component file (the one without a "use client" directive). They are rendered into HTML on the server, and no corresponding component code is sent to the client.
Here’s an example of a custom cell that is processed entirely on the server:
// in your server component file (e.g., app.tsx)
const ServerCustomCell = (props) => {
return (
<td {...props.tdProps}>
<div>{props.children} (Processed on Server)</div>
</td>
);
};
export default function ServerGrid() {
return (
<Grid data={data}>
<GridColumn field="ProductName" title="Product Name" />
<GridColumn field="ProductID" title="ID" cell={ServerCustomCell} />
</Grid>
);
}
This approach is ideal for displaying data that doesn’t require user interaction within the cell itself.
Client Templates for Interactivity
For scenarios requiring interactivity, like using React Hooks or attaching client-side event handlers, we can use client templates. This is achieved by defining our custom cell component in a separate file and marking it with the "use client" directive.
We then import this interactive component into our server component. React will render the initial HTML on the server and then “hydrate” the component on the client, making it fully interactive.
First, we define the interactive component in its own file:
// client-components.tsx
"use client";
import * as React from "react";
export const InteractiveCell = (props) => {
// This cell can now use hooks, state, and client-side events
const [liked, setLiked] = React.useState(false);
return (
<td {...props.tdProps}>
{props.dataItem.ProductName}
<button onClick={() => setLiked(!liked)}>{liked ? "❤️" : "🤍"}</button>
</td>
);
};
Next, we import and use it in our server component:
// in your server component file (e.g., app.tsx)
import { InteractiveCell } from "./client-components";
export default function ServerGrid() {
return (
<Grid data={data}>
<GridColumn
field="ProductName"
title="Product Name"
cell={InteractiveCell}
/>
<GridColumn field="ProductID" title="ID" />
</Grid>
);
}
This hybrid model gives us the power to optimize for performance or interactivity on a component-by-component basis.
Wrap-up
RSCs are introducing a new way we build React applications, and the KendoReact team is embracing this shift. The new RSC mode for the KendoReact Data Grid provides a way to build high-performance, scalable applications by moving data-intensive operations to the server.
To get started and learn more about the specifics, check out the official Getting Started with the KendoReact Grid RSC Mode documentation!
Remember: The DataGrid RSC Mode is available as part of KendoReact Free. Download now to get started:

Hassan Djirdeh
Hassan is a senior frontend engineer and has helped build large production applications at-scale at organizations like Doordash, Instacart and Shopify. Hassan is also a published author and course instructor where he’s helped thousands of students learn in-depth frontend engineering skills like React, Vue, TypeScript, and GraphQL.

