Using Conditions and Actions
A rule in Fiddler Everywhere is a feature that enables you to use a condition to match targeted traffic (HTTP requests and responses) and then apply a specific action to modify its original behavior.
The article lists and explains the supported matching conditions and applicable actions while creating a rule with the Rules tab in Fiddler Everywhere. It also covers the specifics of final and non-final actions and their immediate result on the modified traffic.
Conditions
The Rule Builder can add and use single or multiple matching conditions needed to trigger different actions. The conditions are logical structures with different statements whose numbers can vary between two and four. A statement field that handles text (string modifier) is case-insensitive by default (you can use the Aa button to change them to case-sensitive) and can be auto-completed with suggestions corresponding to the captured sessions.
For more information, refer to the following list.
| Condition Value | Field Options | Field Options | Field Options | Usage Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Sessions | n/a | n/a | n/a | Matches all captured sessions |
| URL | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific keyword in the URL column. |
| Host | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific keyword in the Host column. |
| Path | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific keyword in the path column. |
| Protocol | HTTP, WebSocket, Socket.IO, RPC, gRPC, SSE | n/a | n/a | Differentiate the traffic based on the used protocol |
| Method | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches sessions using specific HTTP Method. |
| Status Code | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific keyword in the Result column. |
| HTTP Version | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific HTTP Version. |
| Request Header | Header name | String modifiers | The search value | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the explicitly mentioned Request header column. |
| Response Header | Header name | String modifiers | The search value | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the explicitly mentioned Response header column. |
| Request Body | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the Request Body column. |
| Response Body | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the Response body. |
| Request Cookie | Cookie name | String modifiers | Search value | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the explicitly mentioned Request Cookie. |
| Response Cookie | Cookie name | String modifiers | Search value | Matches sessions with specific keyword in the explicitly mentioned Response Cookie. |
| Request Body Size | Number modifiers (compares bytes) | Search value | n/a | Matches session with specific Request Body Size. |
| Response Body Size | Number modifiers (compares bytes) | Search value | n/a | Matches session with specific Response Body Size. |
| Request Time | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches specific date string in the Request Time column. |
| Request Date | Date modifiers | Date form | n/a | Matches session executed on a specific date. |
| Duration | Number modifiers (compares milliseconds) | Search value | n/a | Matches sessions with specific Duration. |
| Client IP | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches session with specific Client IP. |
| Remote IP | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches session with specific Remote IP. |
| Certificate Information | Field name | String modifiers | Search value | Matches HTTP responses with specific keyword in the explicitly mentioned certificate field. |
| TLS Version | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches traffic based on the used TLS Version. |
| Process | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches a specific Process ID. |
| Comment | String modifiers | Search value | n/a | Matches sessions with specific Comment column. |
| Rules Modified | Boolean | n/a | n/a | Matches sessions modified by a rule. |
| Magic String | The "magic string" content | n/a | n/a | Uses the legacy Fiddler Classic string literals and regular expressions. |
Actions
When Fiddler Everywhere identifies a request that matches the rule's conditions, it automatically maps it to the action set in the rule. An action field that handles text (string modifier) is case-insensitive by default (you can use the Aa button to change them to case-sensitive) and can be auto-completed with suggestions corresponding to the captured sessions. Note that multiple actions will be executed in their numbered order, and action with the final action type will prevent the execution of all subsequent actions. All actions in Fiddler Everywhere can be dragged and dropped to change their execution priority and each action can be quickly duplicated or deleted (thorugh dedicated buttons).
Apart from returning files or predefined responses, a rule in Fiddler Everywhere can perform the following specific actions:
| Action name | Field Options | Field Options | Preview box | Usage Description | Action type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mark Session | Choose background color | Choose foreground color | Sample Preview box | Marks the session with selected colors. | Non-final |
| Update URL | Value modifiers | New value | n/a | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the current URL. Does not work for CONNECT requests | Non-final |
| Update Query String | Query Parameter Key | Value modifiers | New value | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the query parameters. | Non-final |
| Update Status Code | n/a | n/a | n/a | Modifies the status code returned by the server while preserving the other data untouched. | Non-final |
| Update Request Header | Header Name | Value modifiers | New value | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the request header. | Non-final |
| Update Response Header | Header Name | Value modifiers | New value | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the response header. | Non-final |
| Update Request Body | Value modifiers | New value | n/a | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the request body. | Non-final |
| Update Response Body | Value modifiers | New value | n/a | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the response body. | Non-final |
| Update Request Cookies | Cookie Key | Value modifiers | New value | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the cookie value. | Non-final |
| Update Response Cookies | Cookie Key | Value modifiers | New value | Uses the selected value modifier and the new value to update the cookie value. | Non-final |
| Set Request Breakpoint | Before Sending a Request> | n/a | n/a | Pauses the session before the sending request from Fiddler to the targeted server. The action works only for newly established connections. | Non-final. |
| Set Response Breakpoint | Before Sending a Request | n/a | n/a | Pauses the session before the sending the response from Fiddler to the client application. The action works only for newly established connections. | Non-final. |
| Return File | File Picker | n/a | n/a | Returns the picked response file. | Final |
| Return Manual Response | Text field for creating manual response | n/a | n/a | Returns the manually created response. | Final |
| Return Predefined Response | Predefined responses | n/a | n/a | Returns the selected predefined response. | Final |
| Return CONNECT Tunnel | n/a | n/a | n/a | This action should be used when you wish to test a URL, which will not be resolved by your DNS Server. The option is also reffered as "Accept all CONNECTs". This action is incompatible with sessions snapshots (saved traffic). | Final |
| Do Not Show | n/a | n/a | n/a | Hides the matched session for appearing in Fiddler. When the Do Not Show action is applied, no other actions will be executed. | Final |
| Do Not Decrypt | n/a | n/a | n/a | Skips decryption for a matched session and shows only CONNECT tunnels. Compatible with the following conditions: All Sessions, URL, Host, Scheme, Client IP, Process. The action works only for newly established connections. | Final |
| Close Gracefully | n/a | n/a | n/a | This action will close the connection gracefully. | Final |
| Close Non Gracefully | n/a | n/a | n/a | This action will close the connection forcefully. | Final |
| Delay Request | Number value (milliseconds) | n/a | n/a | Delays the request execution with "n" milliseconds. | Non-final |
| Comment | String modifiers | New value | n/a | Action to modify, add, or remove a session comment | Non-final |
| Magic String | The "magic string" content | n/a | n/a | Uses the legacy Fiddler Classic string literals and regular expressions. | Non-final |
Final and Non-Final Actions
Rule actions can be divided into final and non-final depending on their behavior and whether their presence will allow our actions and rules to be executed. By default, some actions are already final (refer to the detailed actions comparison table above). However, each non-final action can be explicitly made final through the dedicated checkbox "Stop processing more rules" while creating the action in the rules builder.
When you work with final and non-final actions, take into consideration the following insights:
- Final actions prevent the execution of any other actions in the same rule.
- Final actions prevent the execution of any other rule with lower priority (placed lower in the Rules list).
- Final actions are valid (as final) only when the rule matches an HTTP(S) session.
- If a session matches with conditions that depend on its response (for example, a response body contains "HTML"), then any final action in any rule that matches the session will be ignored. The reason for this behavior is that final actions replace the response. By design, Fiddler is not intended to replace a response that was already received and matched conditions in a rule.
- Non-final actions are non-blocking - they will allow actions from any other active rules to execute.
- A non-final action can be explicitly made final by checking the "Make this action final" option.
The following table demonstrate what happens when you combine final and non-final actions in one or multiple rules.
| Actions Type | Result |
|---|---|
| Only non-final actions | All matching rules have their actions performed and applied |
| Only final actions | When a final action triggers, the execution of the rule immediately stops. No other demoted actions or rules will be executed after that. For example, Do Not Show and Do Not Decrypt are final actions. |
| Mix of final and non-final Actions | When a final action triggers, the execution of the rule immediately stops. No other demoted actions or rules will be executed after that (but promoted actions & rules won't be blocked). |
When mixing non-final and final actions, note that their behavior also varies depending on the moment of execution. For example, assume you have a promoted non-final rule A based on a response matching condition. Then, we also have a demoted final rule B based on a request matching condition. The executing logic will be as follows:
- During the request phase, Fiddler skips the non-final rule A (no match), executes the final rule B, and then stops executing further actions.
- During the response phase, Fiddler will execute non-final rule A (as it now matches). Since rule B is final and was already executed, Fiddler will stop executing further actions & rules.
As a result, the session will bear the action from non-final rule A, even though the final rule B was with lower priority. This is because the final action only blocks the execution of further actions and rules but does not block the execution of actions and rules that come before it.
Matching Conditions Specifics
When creating a matching condition in Fiddler Everywhere, you should consider the following:
- Fiddler Everywhere will try to match each session before a request is sent to the server (Fiddler receives requests > match > Fiddler forwards the request to the server) and before a response is sent to the client (Fiddler receives response > match > Fiddler forwards the response to the client app)
- Match conditions will be tested when all the information is available. For example, match conditions that only require data available for the requests are tested before the request is sent to the server. On the contrary, match conditions that depend on a value from the response are tested before returning the response.
- All rules and their matching conditions are tested in order of appearance from top to bottom.
- If a rule contains a matching condition related to a response but contains actions related to the request, then the specific action will be executed after the server receives the request, and all changes will be visible in Fiddler Everywhere only. The user receives a warning within the UI about the above behavior.
- Each rule's matching conditions are tested on the applied changes from the previous rule's executed actions.
Actions and Rules Execution Specifics
Multiple rules enable you to create complex logic that mocks, modifies, and tests your upcoming and outgoing traffic. Sometimes, you will also need to create a combination of the above actions. This section highlights some specifics you must consider while executing multiple rules and actions.
- Each rule will execute independently.
- No rules can block the execution of other rules.
- All actions in this rule will be executed once a rule matches (through the set matching conditions).
An example of the above statement: A rule with matching conditions on the HTTP request and actions on the HTTP response will match before sending the request, and the actions will be applied before returning the response.
- All actions in a rule are executed in the order of appearance, from top to bottom. Actions can be dragged and dropped to change their execution priority.
- If a final action executes, the rules' processing on these sessions stops immediately. Fiddler won't process and perform any other rules or actions (even in the same rule).
- If a rule's actions are incorrectly ordered and a response action is before a request action, the request action will be executed after the server receives the request. The changes will be visible in Fiddler only.
- Actions placed after a final action in one rule will not be executed.
- The Return File, Return Manual Response and Return Predefined Response actions do not execute any connection to the server, they immediately set the HTTP response to the specified value.
- If you execute multiple rules that modify the same thing in the session, the Fiddler will execute both rules in the order they have been set and change the state of the session with each rule action.
- If you execute rules based on the results of other rules, Fiddler will execute only the first rule. The second, third, etc., will not be executed because the condition they use to test the session has changed, and there will be no match.
Rules Order
Note that each rule is prioritized in the Rules list and can be demoted and promoted, which will change the execution order. Final rules won't block other active rules that have higher priority the Rules list.
For an illustration of this scenario, refer to the following cases:
- You have a rule with a final action (for example, the Close Gracefully final action).
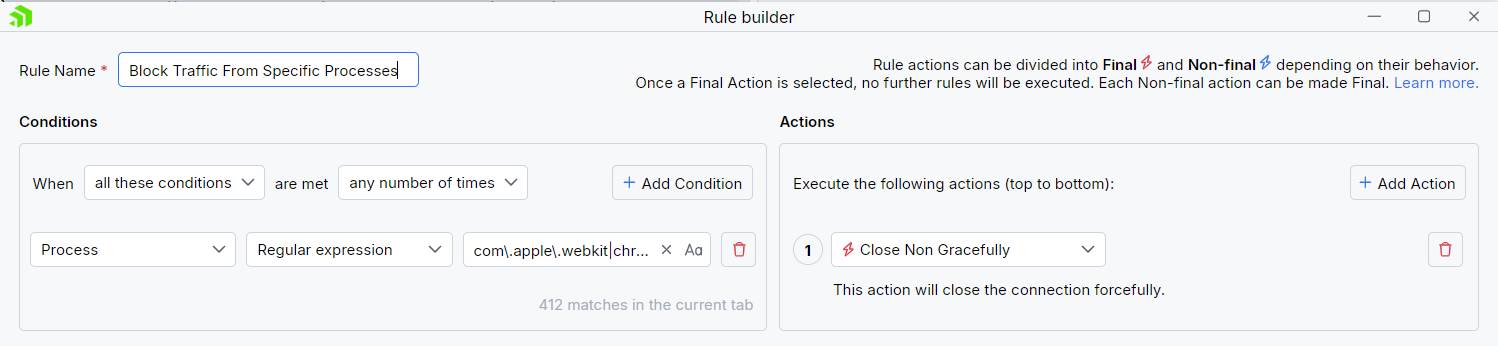
In this case, the rule containing the final action has higher priority in the Rules list. When the matching request is made, only the first rule will execute, and other demoted rules (and actions) will not be triggered.
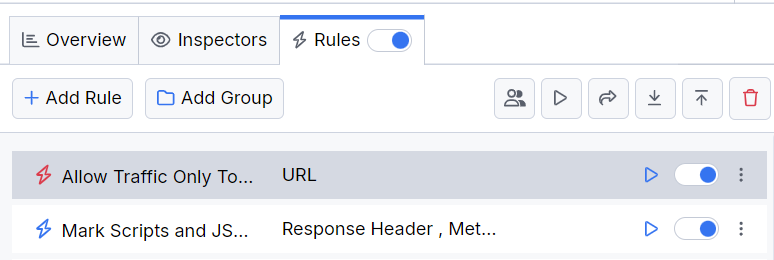
- You have a rule with non-final action (for example, the Mark Session action).
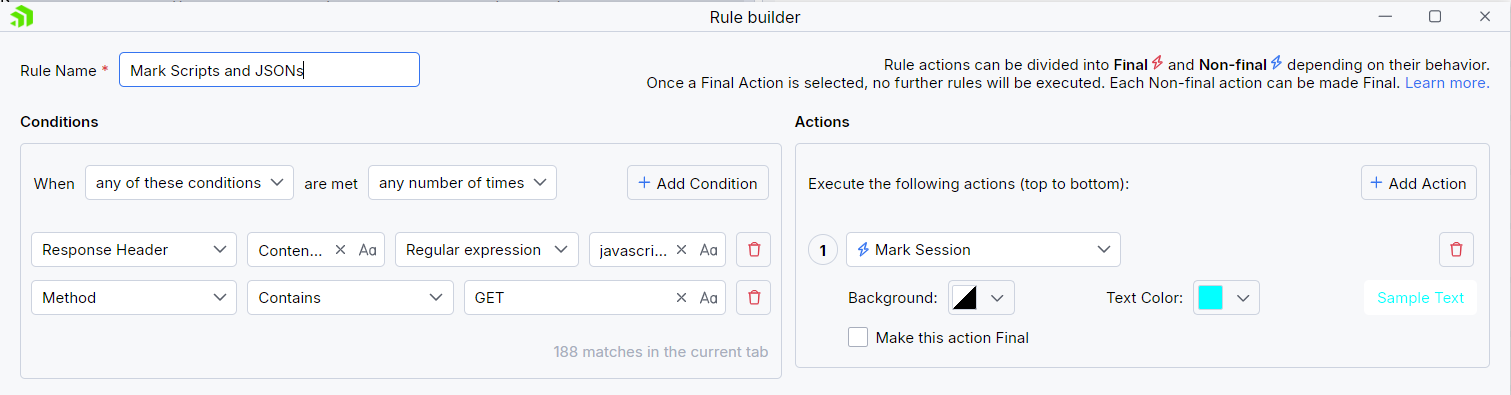
In this case, the rule containing the non-final action has higher priority in the Rules list. When the matching request is made, the non-final action will execute, and then the following demoted rule will be triggered as well. If you add additional rules after the rule that contains final actions, they won't be executed.