Blob Storage
Azure Blob storage is a service for storing large amounts of unstructured object data, such as text or binary data, that can be accessed from anywhere in the world via HTTP or HTTPS. You can use Blob storage to expose data publicly to the world, or to store application data privately. This article will demonstrate how one can use this service from a WPF application and manage the uploaded files.
Set up storage account
For the purposes of this article, you will have to create an Azure Blob Storage account.
Step 1: Create the WPF Application
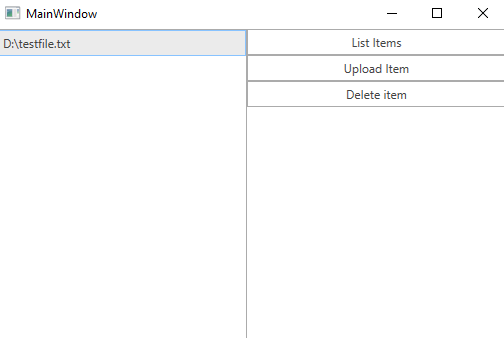
Create a standard WPF application and add 3 RadButtons and a RadListBox to it. The first button will list all of the files uploaded in our storage. The second button will upload a file and the third one will delete the selected file in the RadListBox.
Example 1: Defining the view
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="250" />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<telerik:RadListBox x:Name="radListBox" ItemsSource="{Binding FileNames}" SelectedItem="{Binding SelectedItem, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<Grid Grid.Column="1">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<telerik:RadButton Command="{Binding ListItemsCommand}" Content="List Items"/>
<telerik:RadButton Command="{Binding UploadItemCommand}" Content="Upload Item" Grid.Row="1"/>
<telerik:RadButton Command="{Binding DeleteItemCommand}" Content="Delete item" Grid.Row="2"/>
</Grid>
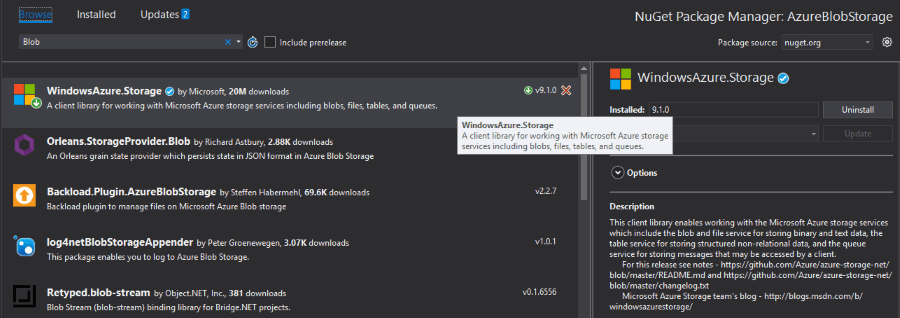
</Grid>Step 2: Install the NuGet package
Open the NuGet Package Manager and install the WindowsAzure.Storage package.
Step 3: Define the ViewModel
The next step is to create the ViewModel. It will need an CloudStorageAccount, CloudBlobContainer and a CloudBlobClient which will be used for connecting to your storage account and for managing the data. We also need to implement all of the commands that the RadButtons are bound to.
Example 2: Defining the ViewModel
public class ViewModel
{
private string connectionString;
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount;
CloudBlobContainer cloudBlobContainer;
CloudBlobClient cloudBlobClient;
private object selectedItem;
private ObservableCollection<string> fileNames;
private IFileDialogService fileDialogService;
public ViewModel(string connectionString, IFileDialogService fileDialogService)
{
this.fileNames = new ObservableCollection<string>();
this.ListItemsCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnListItems);
this.UploadItemCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnUploadItem);
this.DeleteItemCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnDeleteItem);
this.fileDialogService = fileDialogService;
this.connectionString = connectionString;
if (CloudStorageAccount.TryParse(connectionString, out storageAccount))
{
// Connection string is valid and the storageAccount variable is set
cloudBlobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
// Create a new Container with a unique name
cloudBlobContainer = cloudBlobClient.GetContainerReference("mytestcontainer" + Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
cloudBlobContainer.Create();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Could not connect to storage account");
}
}
public object SelectedItem
{
get { return this.selectedItem; }
set { this.selectedItem = value; }
}
public ObservableCollection<string> FileNames
{
get { return this.fileNames; }
set { this.fileNames = value; }
}
private ICommand listItemsCommand;
public ICommand ListItemsCommand
{
get { return this.listItemsCommand; }
set { this.listItemsCommand = value; }
}
private ICommand deleteItemCommand;
public ICommand DeleteItemCommand
{
get { return this.deleteItemCommand; }
set { this.deleteItemCommand = value; }
}
private ICommand uploadItemCommand;
public ICommand UploadItemCommand
{
get { return this.uploadItemCommand; }
set { this.uploadItemCommand = value; }
}
private void OnDeleteItem(object obj)
{
if (this.SelectedItem == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("Please select an Item");
return;
}
var blockBlob = cloudBlobContainer.GetBlockBlobReference(this.SelectedItem.ToString());
blockBlob.DeleteIfExists();
}
private void OnUploadItem(object obj)
{
var fileName = fileDialogService.OpenFileDialog();
CloudBlockBlob cloudBlockBlob = cloudBlobContainer.GetBlockBlobReference(fileName);
cloudBlockBlob.UploadFromFile(fileName);
}
private void OnListItems(object obj)
{
var blobs = cloudBlobContainer.ListBlobs(useFlatBlobListing: true);
this.FileNames.Clear();
foreach (CloudBlockBlob blob in blobs)
{
this.FileNames.Add(blob.Name);
}
}
}Step 4: Define the OpenFileDialogService
The only thing left is to define the interface through which we are opening the RadOpenFileDialog. We also need to define the implementation of that interface which will simply open a RadOpenFileDialog and return the path of the opened file.
Example 3: Defining the OpenFileDialogService and IFileDialogService
public interface IFileDialogService
{
string OpenFileDialog();
}
public class OpenFileDialogService : IFileDialogService
{
public string OpenFileDialog()
{
RadOpenFileDialog choosefiledialog = new RadOpenFileDialog();
choosefiledialog.Filter = "All Files (*.*)|*.*";
choosefiledialog.FilterIndex = 1;
choosefiledialog.Multiselect = false;
choosefiledialog.ShowDialog();
if (choosefiledialog.DialogResult == true)
{
return choosefiledialog.FileName;
}
return string.Empty;
}
}All that is left is to set the DataContext to our ViewModel and pass an instance of the OpenFileDialogService and the connection string of the storage account.
Example 4: Set the DataContext
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
var connectionString = "myConnectionString";
this.DataContext = new ViewModel(connectionString, new OpenFileDialogService());
}You can find the connection string in the All settings of your storage account in the Access keys section.
Figure 1: Example after uploading a file and listing it in the Office2016 theme