New to Telerik UI for WinForms? Start a free 30-day trial
Negative Area Chart
Updated over 6 months ago
Environment
| Product Version | 2018.1 220 |
| Product | RadChartView for WinForms |
Description
By default the area series are painted from bottom to top (above the horizontal axis). This article shows how you can paint a chart where the area is started from zero. This means that the positive values will go up and the negative down.
Figure 1: Sample Chart
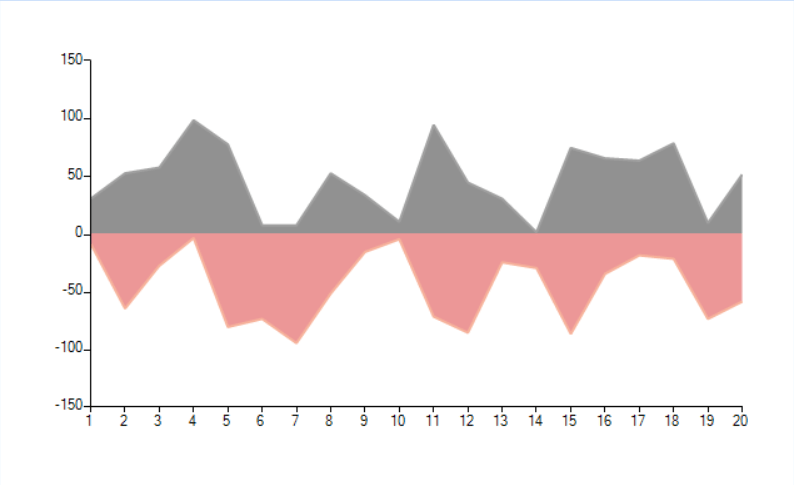
Solution
The solution is to create a custom renderer, and custom draw part which allows you to override the entire painting code. You will use most of the default logic. What you need to change is the Y position of the are rectangle to be on the zero value.
The CustomAreaSeriesDrawPart
C#
class CustomAreaSeriesDrawPart : AreaSeriesDrawPart
{
public CustomAreaSeriesDrawPart(AreaSeries series, ChartRenderer renderer) : base(series, renderer)
{ }
public double GetLocationOfValue(object value, NumericalAxis axis)
{
NumericalAxisModel model = axis.Model as NumericalAxisModel;
double val = Convert.ToDouble(value);
val = (double)model.TransformValue(val);
double delta = axis.ActualRange.Maximum - axis.ActualRange.Minimum;
double normalizedValue = (val - axis.ActualRange.Minimum) / delta;
IChartView view = (IChartView)axis.View;
CartesianArea area = axis.View.GetArea<CartesianArea>();
double result;
if (area != null &&
((area.Orientation == Orientation.Vertical && axis.AxisType == Telerik.Charting.AxisType.First) ||
(area.Orientation == Orientation.Horizontal && axis.AxisType == Telerik.Charting.AxisType.Second)))
{
result = view.PlotOriginX + axis.Model.LayoutSlot.X + normalizedValue * (axis.Model.LayoutSlot.Width * view.ZoomWidth);
}
else
{
result = view.PlotOriginY + ((Telerik.WinControls.UI.ChartView)view).Margin.Top + axis.Model.LayoutSlot.Y + (1.0d - normalizedValue) * (axis.Model.LayoutSlot.Height * view.ZoomHeight);
}
return result;
}
protected override void DrawArea()
{
CartesianRenderer renderer = (CartesianRenderer)this.Renderer;
AreaSeries area = this.Element as AreaSeries;
Graphics graphics = renderer.Graphics;
RadGdiGraphics radGraphics = new RadGdiGraphics(graphics);
RectangleF rect = ChartRenderer.ToRectangleF(this.Element.Model.LayoutSlot);
RectangleF clipRect = (RectangleF)renderer.Area
.GetType()
.GetMethod("GetCartesianClipRect", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic)
.Invoke(renderer.Area, new object[] { });
PointF topLeft = new PointF(clipRect.X, clipRect.Y);
PointF topRight = new PointF(clipRect.Right - 1, clipRect.Y);
PointF lowerRight = new PointF(clipRect.Right - 1, clipRect.Bottom - 1);
PointF lowerLeft = new PointF(clipRect.X, clipRect.Bottom - 1);
List<PointF[]> allPoints = GetPointsPositionsArrays();
float zeroOnTheYAxis = (float)this.GetLocationOfValue(0, (NumericalAxis)area.VerticalAxis);
lowerLeft.Y = zeroOnTheYAxis;
lowerRight.Y = zeroOnTheYAxis;
foreach (PointF[] points in allPoints)
{
if (points.Length < 2)
{
continue;
}
GraphicsPath fillPath = this.GetLinePaths(points);
if (fillPath == null)
{
continue;
}
if (this.Element.View.GetArea<CartesianArea>().Orientation == System.Windows.Forms.Orientation.Vertical)
{
if (area.VerticalAxis.IsInverse)
{
fillPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], new PointF(points[points.Length - 1].X, topRight.Y));
fillPath.AddLine(topRight, topLeft);
fillPath.AddLine(new PointF(points[0].X, topLeft.Y), points[0]);
}
else
{
fillPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], new PointF(points[points.Length - 1].X, lowerRight.Y));
fillPath.AddLine(lowerRight, lowerLeft);
fillPath.AddLine(new PointF(points[0].X, lowerLeft.Y), points[0]);
}
}
else
{
if (area.HorizontalAxis.IsInverse)
{
fillPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], topRight);
fillPath.AddLine(topRight, lowerRight);
fillPath.AddLine(lowerRight, points[0]);
}
else
{
fillPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], topLeft);
fillPath.AddLine(topLeft, lowerLeft);
fillPath.AddLine(lowerLeft, points[0]);
}
}
FillPrimitiveImpl fill = new FillPrimitiveImpl(this.Element, null);
fill.PaintFill(radGraphics, fillPath, clipRect);
GraphicsPath borderPath = new GraphicsPath();
AreaSeries series = (AreaSeries)this.Element;
borderPath = new GraphicsPath();
if (series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.All ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.AllButPlotLine ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.LeftAndPoints ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.LeftLine)
{
if (this.Element.View.GetArea<CartesianArea>().Orientation == System.Windows.Forms.Orientation.Vertical)
{
if (area.VerticalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(topLeft, points[0]);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(lowerLeft, points[0]);
}
}
else
{
if (area.HorizontalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(lowerRight, points[0]);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(lowerLeft, points[0]);
}
}
}
if (series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.All ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.AllButPlotLine ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.LeftAndPoints ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.Points ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.RightAndPoints)
{
GraphicsPath path = GetLinePaths(points);
if (path != null)
{
borderPath.AddPath(path, true);
}
}
if (series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.All ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.AllButPlotLine ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.RightAndPoints ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.RightLine)
{
if (this.Element.View.GetArea<CartesianArea>().Orientation == System.Windows.Forms.Orientation.Vertical)
{
if (area.VerticalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], topRight);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], lowerRight);
}
}
else
{
if (area.HorizontalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], topRight);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(points[points.Length - 1], topLeft);
}
}
}
if (series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.All ||
series.StrokeMode == AreaSeriesStrokeMode.PlotLine)
{
if (this.Element.View.GetArea<CartesianArea>().Orientation == System.Windows.Forms.Orientation.Vertical)
{
if (area.VerticalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(topRight, topLeft);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(lowerRight, lowerLeft);
}
}
else
{
if (area.HorizontalAxis.IsInverse)
{
borderPath.AddLine(topRight, lowerRight);
}
else
{
borderPath.AddLine(lowerLeft, topLeft);
}
}
}
BorderPrimitiveImpl border = new BorderPrimitiveImpl(this.Element, null);
border.PaintBorder(radGraphics, null, borderPath, rect);
if (series.Image != null)
{
graphics.SetClip(fillPath);
ImagePrimitiveImpl image = new ImagePrimitiveImpl(series);
image.PaintImage(radGraphics, series.Image, clipRect, series.ImageLayout, series.ImageAlignment, series.ImageOpacity, false);
graphics.ResetClip();
}
}
}
}
Now you are need to change the default draw part within the custom renderer class.
The Custom Renderer
C#
public class CustomCartesianRenderer : CartesianRenderer
{
public CustomCartesianRenderer(CartesianArea area)
: base(area)
{ }
protected override void Initialize()
{
base.Initialize();
for (int i = 0; i < this.DrawParts.Count; i++)
{
AreaSeriesDrawPart linePart = this.DrawParts[i] as AreaSeriesDrawPart;
if (linePart != null)
{
this.DrawParts[i] = new CustomAreaSeriesDrawPart((AreaSeries)linePart.Element, this);
}
}
}
}
The final step is to setup the chart and change the defualt renderer.
Setup the ChartView
C#
public NegativeAreaChart()
{
InitializeComponent();
radChartView1.CreateRenderer += RadChartView1_CreateRenderer;
AreaSeries areaSeries = new AreaSeries();
// areaSeries.Spline = true;
AreaSeries areaSeries2 = new AreaSeries();
for (int x = 0; x < 60; x++)
{
areaSeries.DataPoints.Add(rnd.Next(1, 100), x);
areaSeries2.DataPoints.Add(rnd.Next(1, 100) * -1, x);
}
this.radChartView1.Series.Add(areaSeries);
this.radChartView1.Series.Add(areaSeries2);
}
private void RadChartView1_CreateRenderer(object sender, ChartViewCreateRendererEventArgs e)
{
e.Renderer = new CustomCartesianRenderer(e.Area as CartesianArea);
}
A complete solution is available in our SDK repository.