Dynamo DB
This article will show you how to create a WinForms application and access data stored in a DynamoDB table. It shows how you can connect to the AWS DynamoDB service from a blank WinForms project as well.
Please note that you can use the local version of DynamoDB to setup and test your application. This article shows a real example.
Step 1: Create a WinForms project.
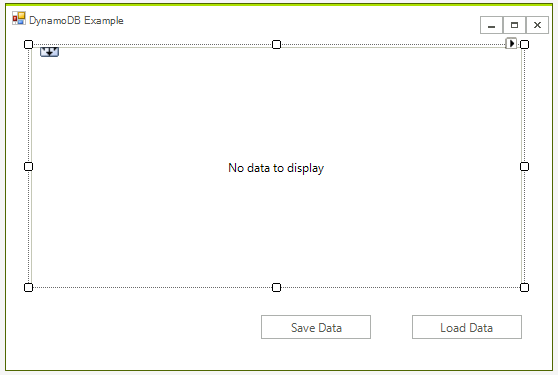
First create the WinForms project, to do that create a blank Telerik UI for WinForms project and add a RadGridView and two buttons to it. The application design should look like this:
Step 2: Install the NuGet package
In Visual Studio open the NuGet package manager and install the DynamoDB module:
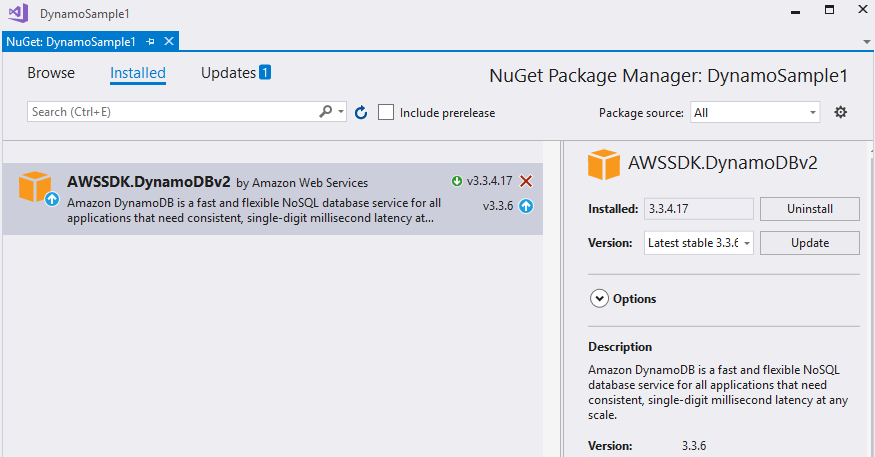
Another option is to to type the following command in the NuGet Package Manager Console: PM> Install-Package AWSSDK.DynamoDBv2
In addition you need to add the following to your App.config file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="AWSProfileName" value="Telerik"/>
<add key="AWSRegion" value="eu-west-3" />
</appSettings>
</configuration>
If you do not have a AWS account in Visual Studio please check the Getting Started article.
Step 3: Create the AWS manager class
Add a class called AWS_Manager to the example. You will use this class to add all functionality for managing the DynamoDB database. For now you can create the method that crates the table:
class AWS_Manager
{
AmazonDynamoDBClient client;
public AWS_Manager()
{
try
{
client = new AmazonDynamoDBClient();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
RadMessageBox.Show("Error: failed to create a DynamoDB client; " + ex.Message);
}
}
public void CreateTable()
{
List<string> currentTables = client.ListTables().TableNames;
if (!currentTables.Contains("Customers"))
{
CreateTableRequest createRequest = new CreateTableRequest
{
TableName = "Customers",
AttributeDefinitions = new List<AttributeDefinition>()
{
new AttributeDefinition
{
AttributeName = "Id",
AttributeType = "N"
},
new AttributeDefinition
{
AttributeName = "Name",
AttributeType = "S"
}
},
KeySchema = new List<KeySchemaElement>()
{
new KeySchemaElement
{
AttributeName = "Id",
KeyType = "HASH"
},
new KeySchemaElement
{
AttributeName = "Name",
KeyType = "RANGE"
}
},
};
createRequest.ProvisionedThroughput = new ProvisionedThroughput(1, 1);
CreateTableResponse createResponse;
try
{
createResponse = client.CreateTable(createRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
RadMessageBox.Show("Error: failed to create the new table; " + ex.Message);
return;
}
}
}
}Now when the table is ready you can add some data, add the following method to the AWS_Manager class:
public void AddData()
{
Table table = Table.LoadTable(client, "Customers");
if (table.Keys.Count == 0)
{
Document dataObj1 = new Document();
dataObj1["Name"] = "Telerik";
dataObj1["Id"] = 2;
dataObj1["Employees"] = 46;
dataObj1["State"] = "NY";
table.PutItem(dataObj1);
Document dataObj2 = new Document();
dataObj2["Name"] = "Progress";
dataObj2["Id"] = 13;
dataObj2["Employees"] = 54;
dataObj2["State"] = "IL";
table.PutItem(dataObj2);
}
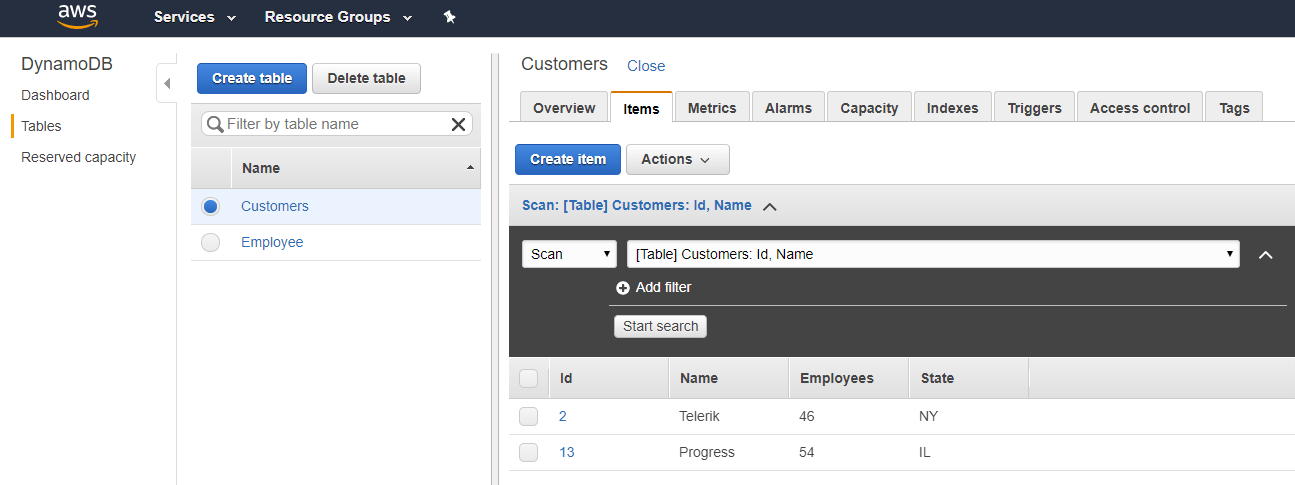
}If you run the code at this point you will be able to see the data in your AWS console:
Step 4: Get the Data from DynamoDb
Now you are ready to populate the grid with the data. Although you can directly populate the grid from the data I believe that is better to have a local business object to store the data.
First you need to get the data. The following method will return a List<Document>, each document represents an entry from the database.
public List<Document> GetData()
{
Table table = Table.LoadTable(client, "Customers");
ScanFilter scanFilter = new ScanFilter();
ScanOperationConfig config = new ScanOperationConfig()
{
Filter = scanFilter,
Select = SelectValues.AllAttributes,
};
Search search = table.Scan(config);
List<Document> documentList = new List<Document>();
do
{
documentList.AddRange(search.GetNextSet());
} while (!search.IsDone);
return documentList;
}We can use the above method to iterate the documents and get the data. Here is the code along with the business object.
private void radButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var data = manager.GetData();
var gridData = new List<Customer>();
foreach (Document doc in data)
{
var customer = new Customer();
foreach (var attribute in doc.GetAttributeNames())
{
var value = doc[attribute];
if (attribute == "Id")
{
customer.Id = Convert.ToInt32(value.AsPrimitive().Value);
}
else if (attribute == "Name")
{
customer.Name = value.AsPrimitive().Value.ToString();
}
else if (attribute == "Employees")
{
customer.Employees = Convert.ToInt32(value.AsPrimitive().Value);
}
else if (attribute == "State")
{
customer.State = value.AsPrimitive().Value.ToString();
}
}
gridData.Add(customer);
}
radGridView1.DataSource = gridData;
}
class Customer
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Employees { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
}
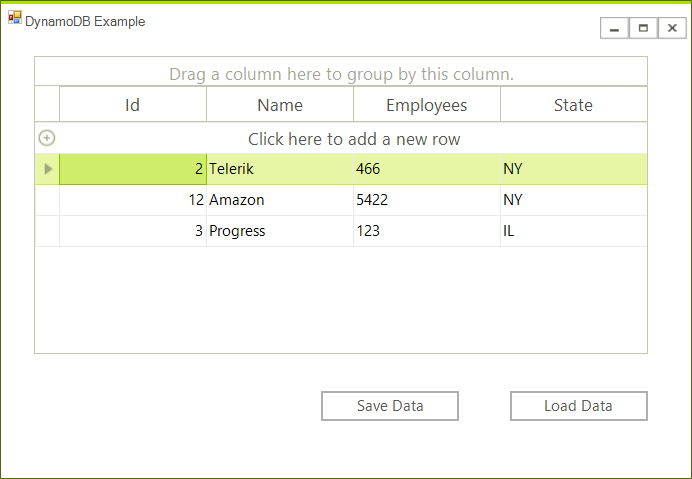
The grid is now populated.
Step: 5 Save the Changes
The final steps is to save the changes. Upon a button click we will iterate all rows and update the items in the database. We will need a function that updates an item in the manager class. Here is the code.
// Main form class
private void radButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
foreach (GridViewDataRowInfo item in radGridView1.Rows)
{
manager.UpdateCustomerEntry(item.DataBoundItem as Customer);
}
}
// AWS_Manager class
public void UpdateCustomerEntry(Customer customer)
{
Table table = Table.LoadTable(client, "Customers");
var entry = new Document();
entry["Id"] = customer.Id;
entry["Name"] = customer.Name;
entry["Employees"] = customer.Employees;
entry["State"] = customer.State;
table.UpdateItem(entry);
}